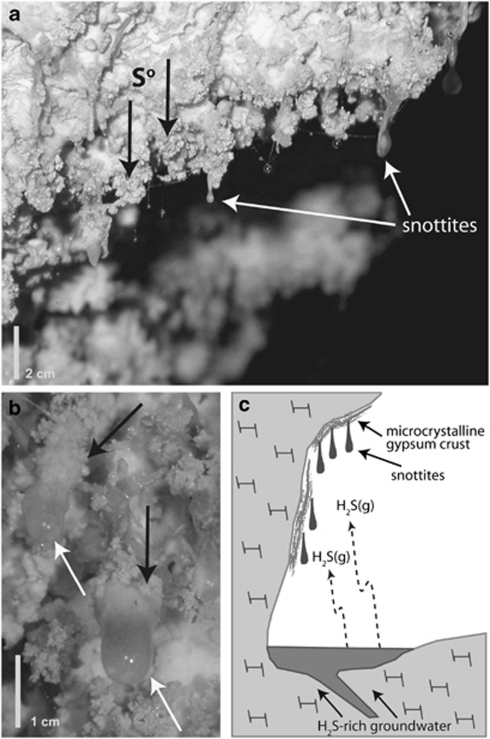
Figure 1.
(a, b) Field photographs of the collection site for snottite sample RS24. Note elemental sulfur (black arrows) occurring in close association with biofilm surfaces. (c) Schematic diagram depicting the formation of sulfidic cave snottites. Snottites form on subaerial cave surfaces in areas exposed to H2S(g) degassing from circumneutral cave streams. Snottites have extremely acidic pH values (0–1), because they are isolated from limestone cave walls and gypsum corrosion residues that would otherwise buffer the pH >2.