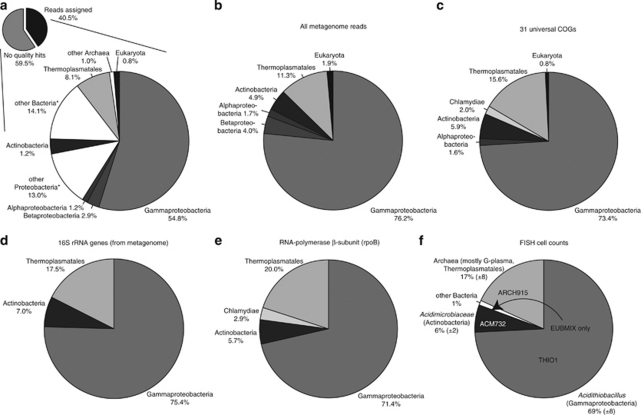
Figure 2.
Comparison of RS24 community composition based on FISH and metagenomic data. (a) Taxonomic classification and binning of all metagenomic reads. Using the criteria described in the methods, 40.5% of total metagenome reads were assigned to taxa. *groups include reads that cannot be assigned to a more specific taxonomic group. Taxa that make up <0.5% of all matches are omitted from the figure. (b) Community composition based on taxonomic classification of all metagenomic reads, after removing reads assigned to non-specific groups (for example, ‘other bacteria'). (c–e) Community composition based on phylogenetic markers from the metagenome: (c) 31 universal genes (Ciccarelli et al., 2006), (d) 16S rRNA genes and (e) RNA polymerase-β subunit sequences. (f) Community composition determined from FISH cell counts. Numbers in parentheses represent one s.d. FISH probes used to generate the data were THIO1, genus Acidithiobacillus, ACM732, Acidimicrobiaceae family, EUBMIX, bacteria and ARCH915, archaea.