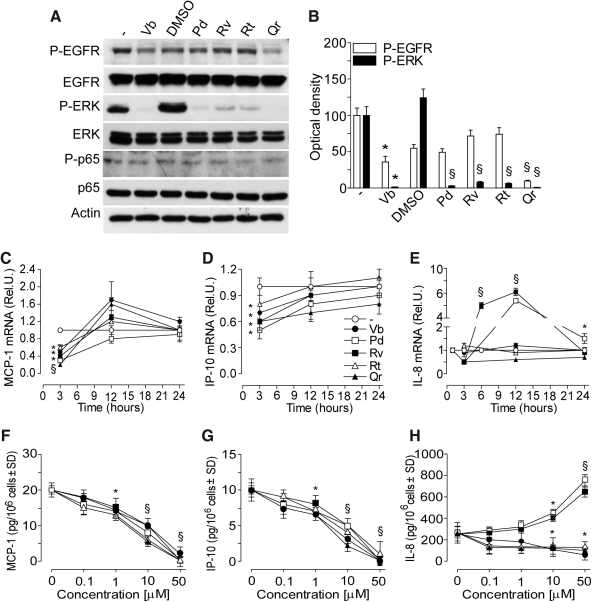
FIG. 2.
PP effects on spontaneous epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)/extracellular regulation kinase (ERK)/p65 phosphorylation, chemokine gene expression, and protein synthesis in normal human epidermal keratinocytes (NHEK). (A) Western blots of EGFR and its phosphorylation form (P-EGFR), of ERK and its phosphorylation form (P-ERK) of p65 and its phosphorylation form (P-p65) after 15 min NHEK incubation with or without 50 μM PPs. (B) Quantification of Western blots by densitometry. *p<0.01 versus untreated control, §p<0.01 versus 0.25% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)-treated conditions. (C–E) Time-dependent spontaneous chemokine gene expression (mRNA, fold induction vs. untreated cultures) affected by incubation of NHEK with 50 μM verbascoside (Vb), resveratrol (Rv), polydatin (Pd), rutin (Rt), or quercetin (Qr). Results are expressed as the mean±SD. *p<0.05 and §p<0.01 versus control. (F–H) Concentration-dependent effects of PPs on spontaneous monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) (F), interferon gamma-produced protein of 10 kDa (IP-10) (G), and interleukin 8 (IL-8) (H) release from NHEK. Measurements were performed 24 h after PPs addition to NHEK. *p<0.05 and §p<0.01 versus control.