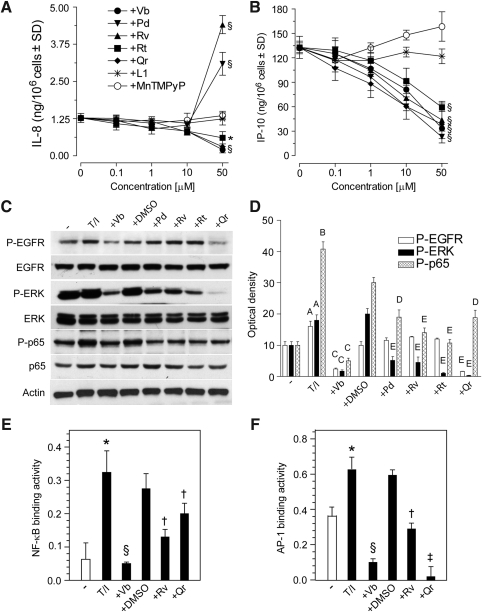
FIG. 5.
PP effects on (tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α] plus IFN-γ)-induced EGFR, ERK, and p65 phosphorylation, chemokine production, and nuclear factor κB (NFκB) and activator protein 1 (AP-1) DNA binding. (A) Concentration-dependent effects of PPs, SOD-mimicking compound (MnTMPyP), and iron chelator (L1) on IL-8 and (B) IP-10 release by NHEK stimulated with TNF-α (100 ng/ml) and IFN-γ (100 U/ml) (T/I) for 24 h. Before T/I addition, NHEK underwent 1 h pretreatment with polyphenols or antioxidants. *p<0.05 and §p<0.01 versus. keratinocytes treated with T/I. (C) Effects of PPs (50 μM, preincubation for 1 h) on EGFR, ERK, and p65 phosphorylation triggered by 15 min stimulation with T/I, and (D) quantification of Western blot bands by densitometry. Ap<0.05 and Bp<0.01 versus untreated controls; Cp<0.01 versus T/I-treated conditions; Dp<0.05 and Ep<0.01 versus T/I+0.25% DMSO-treated conditions. Effects of PPs (50 μM, 1 h preincubation) on T/I-induced (E) NFκB-DNA binding and (F) AP-1-DNA binding. *p<0.01 versus untreated keratinocytes, §p<0.01 versus keratinocytes treated with T/I, †p<0.05 and ‡p<0.01 versus keratinocytes treated with 0.25% DMSO+T/I.