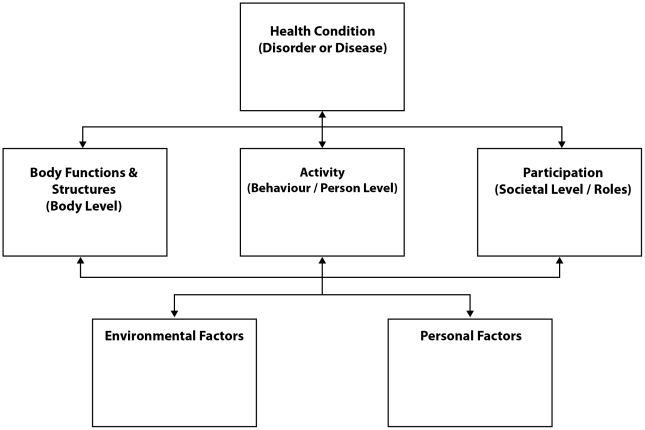
Figure 1. The International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF).
The ICF model [13] presents a social model of health and functioning that is comprised of six inter-related domains: Health Condition, Body Functions and Structures, Activity, Participation, Environmental Factors, and Personal Factors. Health Condition refers to the presence/absence of a disorder or disease. Body Functions and Structure identifies the impact of physical bodily functioning on health. Within this model, health is seen to be not only the absence of a Health Condition, but also the individual's ability to complete daily Activities of necessity and their Participation in important life roles. Health and functioning is influenced by the existence of Environmental Factors (climactic environment, social attitudes, policies, services, etc.) that can be barriers or supports to health and functioning. Personal Factors (poverty, education level, gender, etc.) also influence health and functioning, depending on the environment a person lives within. Health and functioning is seen within this model as being not only an outcome of a health condition, but also of the other five domains that interact. Hence, health and functioning is seen to depend on context (Environment) and Personal Factors as much as the presence of a health condition and impaired body functions and structures. Finally, impairment is seen not only in terms of reduced bodily functions, but also in terms of a person's inability to complete daily activities and/or to participate in important life roles.