Figure 1. Examples for model chromatids with different parameter sets.
The grey tube represents the chromatin fibre. The orange sticks visualize the cross-links between distant fibre segments. Each chain embodies a single chromatid. The chromatin fibre in both examples consisted of 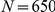 segments. The cutoff length for the loop sizes is
segments. The cutoff length for the loop sizes is  . It means that fibre segments which are separated by a genomic distance greater than 50 monomers cannot form an additional bond. A. In this example, the mean loop concentration is
. It means that fibre segments which are separated by a genomic distance greater than 50 monomers cannot form an additional bond. A. In this example, the mean loop concentration is  . At these low loop concentrations the conformations are non-homogeneous. Rather, a2 formation of blobs can be observed in regions with many cross-links. These regions are connected by fibre section with no or only few loops. B. When the loop concentration is high enough, a condensation of the chromatin fibre into thick, homogeneous rods can be observed. In this configuration the loop concentration is
. At these low loop concentrations the conformations are non-homogeneous. Rather, a2 formation of blobs can be observed in regions with many cross-links. These regions are connected by fibre section with no or only few loops. B. When the loop concentration is high enough, a condensation of the chromatin fibre into thick, homogeneous rods can be observed. In this configuration the loop concentration is  . Cross-links are distributed homogeneously along the chain.
. Cross-links are distributed homogeneously along the chain.

