Figure 1.
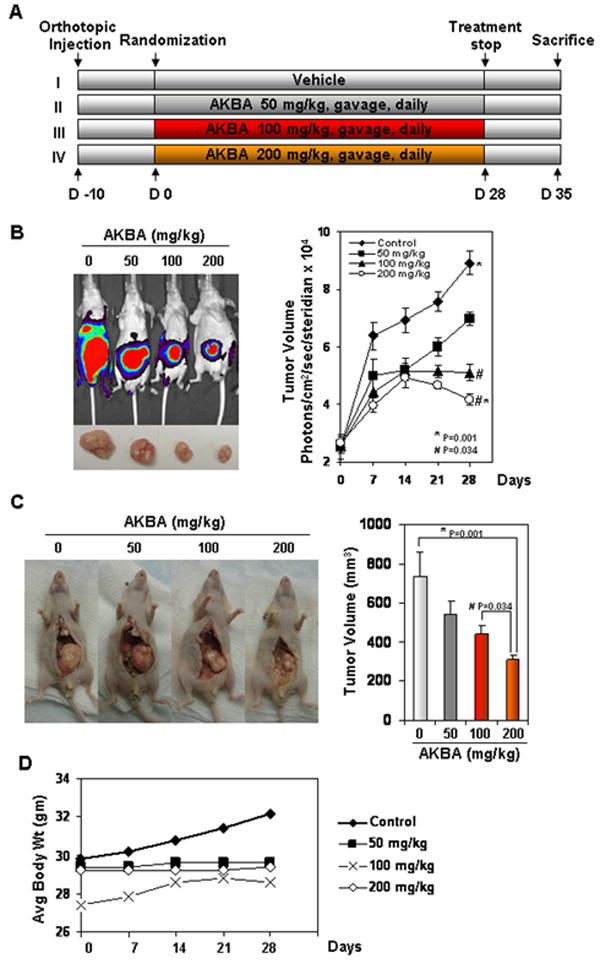
AKBA inhibits the growth of orthotopically implanted CRC tumors in nude mice. (A) Schematic of the experimental protocol described in Materials and Methods. Group I was given corn oil (100 μL orally, daily); Group II was given AKBA (50 mg/kg orally, daily); Group III was given AKBA (100 mg/kg orally, daily); and Group IV was given AKBA (200 mg/kg orally, daily). (B) Bioluminescence imaging of orthotopically implanted CRC in live, anesthetized mice (left panel); measurements (photons/sec) of tumor volume (mean ± standard error) at various time points using live bioluminescence imaging at the indicated times (n = 6) (right panel). (C) Necropsy photographs of mice with orthotopically implanted CRC (left panel); tumor volumes (mean ± standard error; P < 0.001, control vs. 200-mg/kg AKBA and P < 0.034, control vs. 100-mg/kg AKBA) in mice measured on the last day of the experiment at autopsy using Vernier calipers and calculated using the formula V = 2/3 πr3 (n = 6). (D) As shown by the body weight change in mice, AKBA had no toxicity in the amount tested. There was no significant difference in body weight between the treated group and the control group.
