Figure 3.
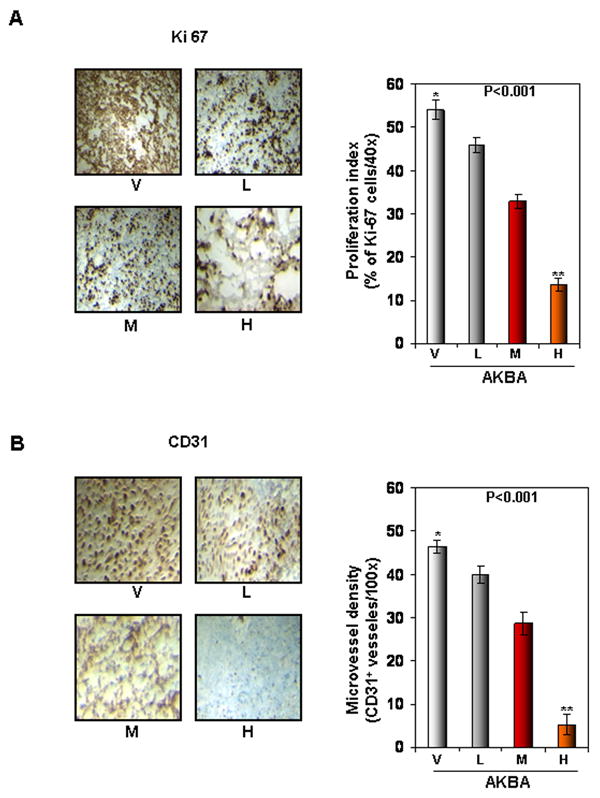
AKBA inhibits tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis in CRC. (A) The results of an IHC analysis of proliferation marker Ki-67 indicated that CRC cell proliferation was inhibited in mice treated with AKBA at different dose concentrations: V, vehicle; L, low (AKBA 50 mg/kg); M, medium (100 mg/kg); and H, high (200 mg/kg) (Left panel). Quantification of Ki-67 cells, as described in Materials and Methods. Values are represented as the mean ± standard error of triplicate (Right panel). (B) The results of an IHC analysis of CD31 for microvessel density indicated that angiogenesis was inhibited by AKBA at different dose concentrations. V, vehicle; L, low (AKBA 50 mg/kg); M, medium (100 mg/kg); and H, high (200 mg/kg) (Left panel). Quantification of CD31-positive microvessel density, as described in Materials and Methods. Values are the mean ± standard error of triplicate.
