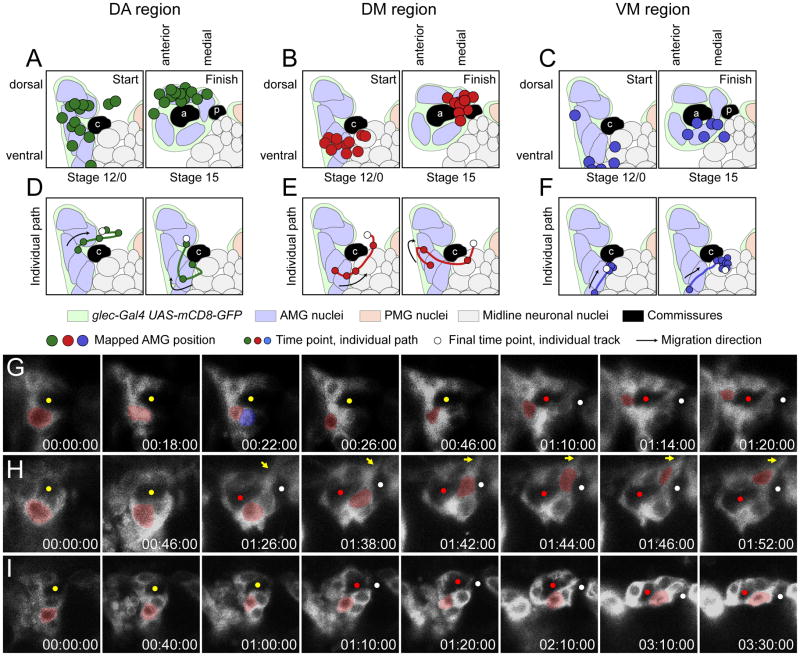
Fig. 5. AMG migrate along stereotypical paths.
(A–C) Schematics of idealized stage 12/0 and stage 15 segments focused on the commissures and the surrounding AMG. The starting and finishing positions of 31 AMG from time-lapse imaging experiments are mapped onto these idealized segments (see Materials and methods). At stage 12/0 there is a single commissure labeled c, and at stage 15 the AC and PC are labeled a and p, respectively. Other symbols are defined in the key. (A) Most AMG that completed their migration above the AC (DA region) started their migration in the most dorsal group of midline cells at stage 12/0 (14 AMG analyzed). (B) AMG that ceased migration above and between the commissures (DM region) began their migration in the intermediate region at stage 12/0 (11 AMG analyzed). One circle is completely obscured by other overlapping circles. (C) Most AMG that migrated to the region below and between the commissures (VM region) started their migration in the most ventral portion of the segment (6 AMG analyzed). (D–F) Two examples of individual AMG migration paths for each position. Paths are drawn on a schematic of stage 12/0, but represent migration during stages 12/0 to 15. (G–I) Time-lapse experiments showing the paths of individual AMG that migrated to the (G) DA, (H) DM, and (I) VM regions. The AMG of interest is pseudocolored in red and elapsed time is shown (hh:mm:ss). Yellow circles mark the single commissures; red and white circles mark the AC and PC. (G) The AMG begins migration below the commissure, divides (red and blue pseudocolor), and migrates internally to the DA region, adjacent to the AC. (H) An AMG pauses for 1 hour and 26 minutes before rapidly (6 min) migrating internally between the commissures to the DM region. Yellow arrow indicates a long process that extends above the midline, presumably emanating from the migrating AMG. (I) This AMG migrates from an external position to contact the AC and stays in the VM region for the remainder of the experiment.