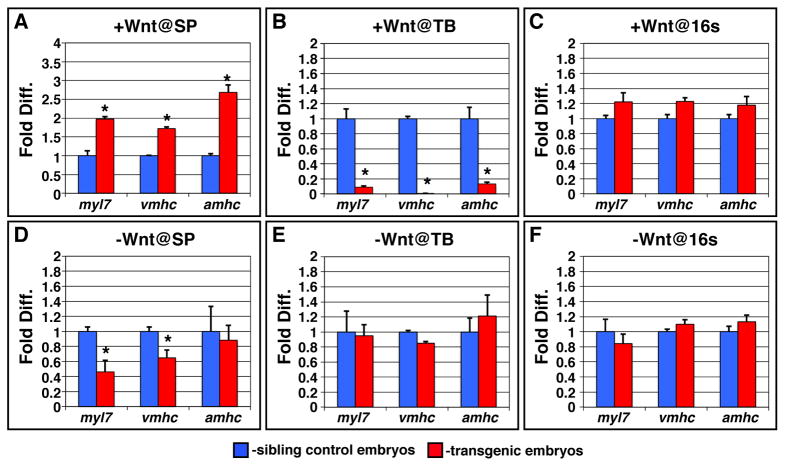
Figure 3. qPCR analysis of myl7, vmhc and amhc expression after modulation of Wnt signaling.
(A) Increasing Wnt signaling at the sphere stage causes an increase in CM differentiation marker gene expression. (B) Increasing Wnt signaling at the TB stage causes a decrease in CM differentiation marker gene expression. (C) Increasing Wnt signaling at the 16s stage does not have a significant effect on CM differentiation marker gene expression. (D) Decreasing Wnt signaling causes a decrease in myl7 and vmhc expression. (E,F) Decreasing Wnt signaling at the TB and 16s stages does not affect CM differentiation marker gene expression. Analysis of gene expression was performed on embryos at the 20–22s stages. All trends of expression examined with qPCR, except for amhc after decreasing Wnt signaling at sphere, are similar to those observed in Figs. 1 and 2 with quantification by ISH area. The inability to detect a decrease in amhc expression could be due to the higher variability of amhc observed in both control and transgenic embryos. Although vmhc is also expressed in the somites, trends with respect to expression closely parallel those observed in the heart. However, we cannot rule out that the trends observed reflect additional effects of Wnt signaling on vmhc in the somites. Error bars for all qPCR analysis indicate the standard deviation of the triplicates used for analysis. Asterisks for all qPCR experiments indicate a statistically significant difference (p<0.05) in expression using Student’s t-test.