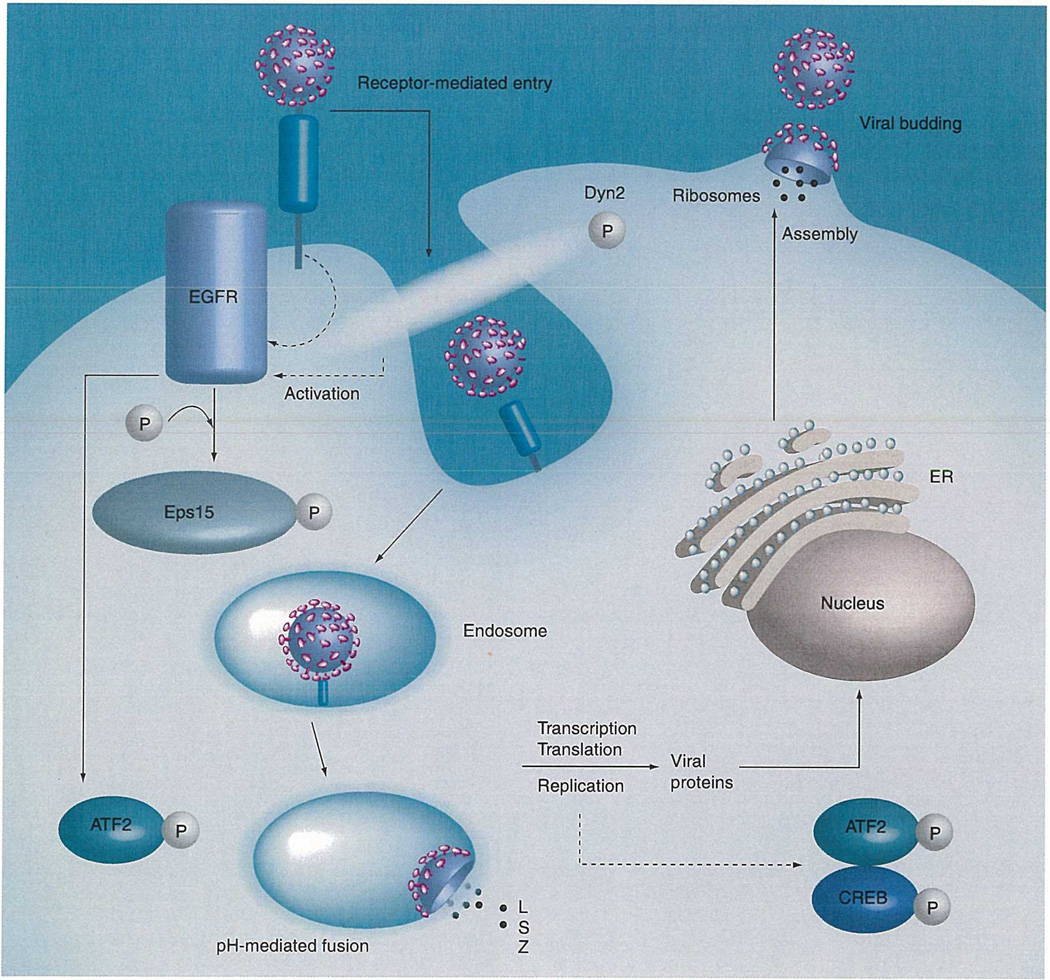
Figure 1. Arenavirus entry/replication cycle.
This figure represents the arenavirus entry/replication cycle and illustrates possible involvements of proteins and phosphorylation events. EGFR may be activated through receptor binding or by the endosomal entry process (the hypothesized activation is represented by dashed lines). Activation of EGFR likely leads to the phosphorylation of Eps15, which is required for arenavirus endosomal entry, as well as downstream phosphorylation events of ATF2. The phosphorylation of Dyn2 is also likely required for clathrin-mediated endosomal entry of arenaviruses. Additionally, the phosphorylation of ATF2 and CREB may be caused by viral replication, which eventually leads to cell stress. The dotted lines represent hypothesized activation or the involvement of proteins, while the solid lines represent the involvement of proteins or the trafficking of arenaviruses through the replication cycle.
EGFR: EGF receptor; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; L: Large protein; S: Small protein; Z; RING finger Z protein.