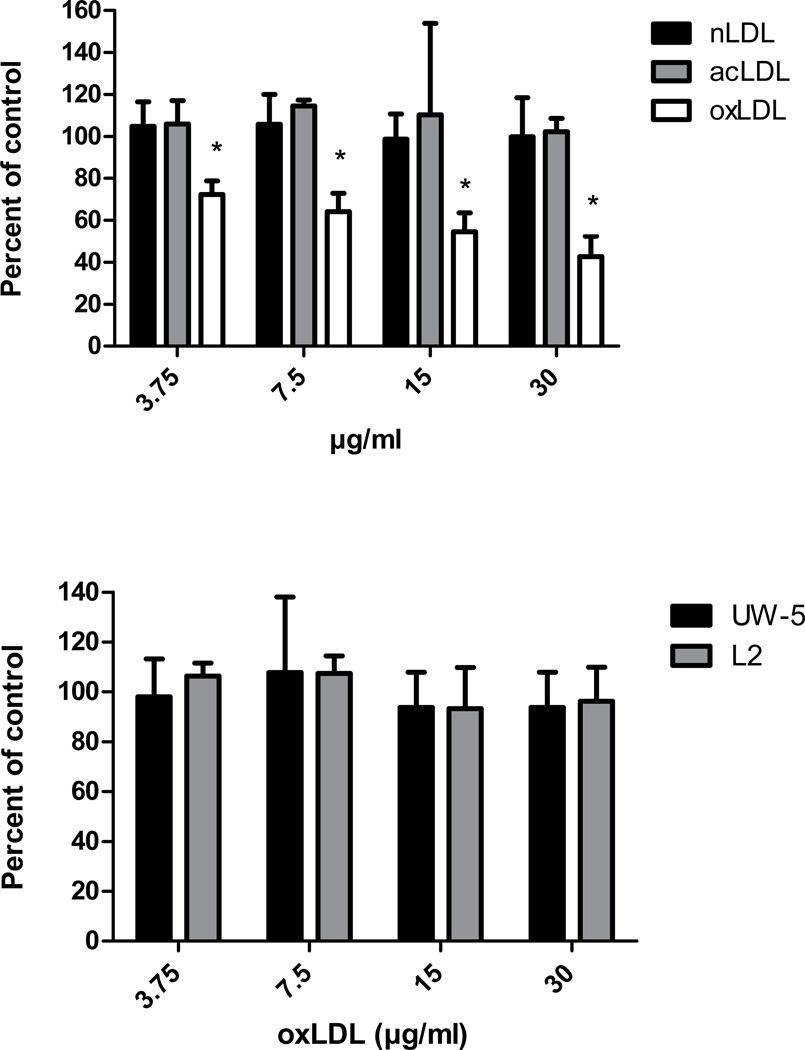
Fig. 1.
Effects of LDLs on Chlamydia pneumoniae infectivity of endothelial cells. Endothelial cells (HMEC-1) were incubated with 0.2 ml of the indicated LDL concentrations or PBS for 1 hr prior to infection. Infectivity titers were determined by inclusion counts following staining with the Chlamydia genus specific antibody CF-2. Infectivity titers (inclusion counts) of LDL treated cells were compared with PBS treated cells (control) and are denoted as percent of control on the y axis. Panel A - effect of native LDL (n-LDL), acetylated LDL (ac-LDL) and oxidized LDL (ox-LDL) on C. pneumoniae infectivity (three coverslips were counted per concentration tested). Panel B - effect of ox-LDL on C. trachomatis serovars E (UW-5) and L2 (three coverslips were counted per concentration tested). A representative experiment is shown.