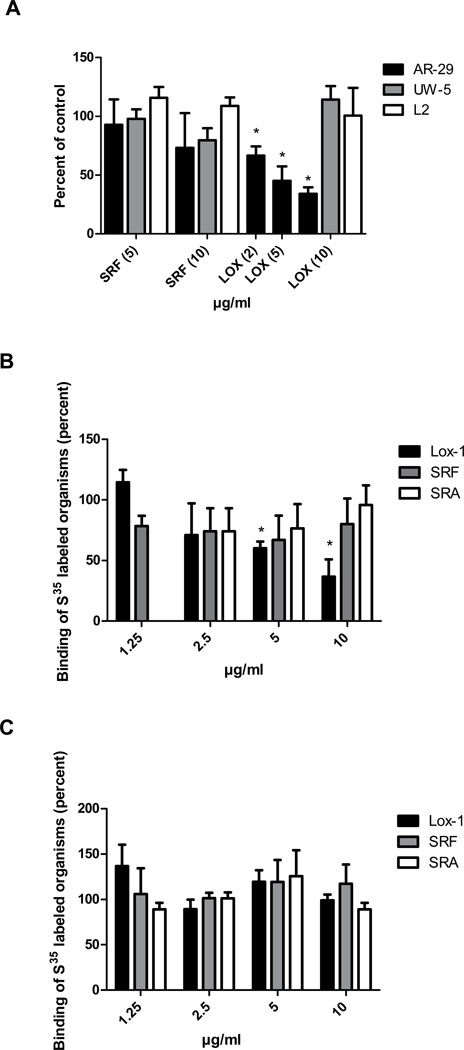
Fig. 3.
LOX-1 monoclonal antibody inhibits attachment and infectivity of Chlamydia pneumoniae. Panel A. Effects of antibodies against different classes of scavenger receptors on C. pneumoniae infectivity. Endothelial cells (HMEC-1) were incubated with 0.2 ml of the indicated antibody concentrations or PBS for 1 hour prior to infection. Infectivity titers were determined by inclusion counts following staining with the Chlamydia genus specific antibody CF-2. Infectivity titers of antibody treated cells were compared with PBS treated cells (control) and are indicated as percent of the control. Three coverslips were counted for each assay. Panel B. Binding assays using metabolically labeled C. pneumoniae (AR-39) organisms. Endothelial cells were incubated for 1 hr with anti-LOX-1, anti-SRA, anti-SREC-I receptor antibody or PBS. Subsequently, cells were inoculated with radiolabeled organisms at 4°C (organisms attach, but are not internalized). After washing of cells, radioactive counts were determined. Assays were done in triplicate. Panel C. Binding assays using metabolically labeled C. trachomatis (UW-5) organisms. Binding assays were done as described in Panel B. A representative experiment is shown.