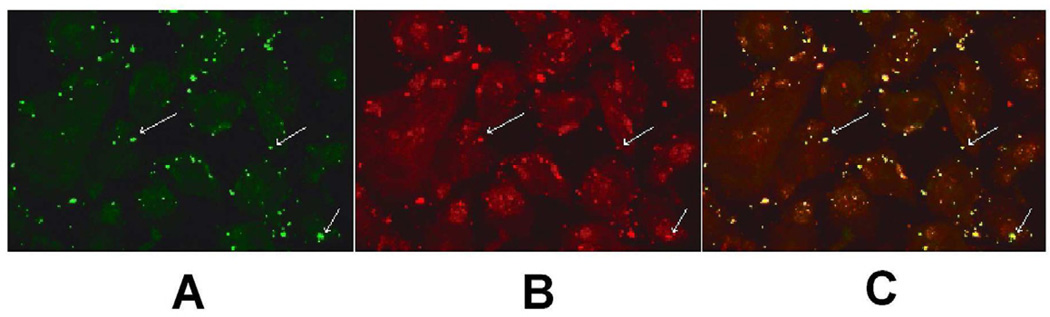
Fig. 4.
C. pneumonaie colocalizes with the LOX-1 receptor. Endothelial cells were inoculated with C. pneumoniae at 4°C for 30 min to permit attachment, but not internalization. Following fixation of cells, double immunofluorescence labeling of infected cells was done by staining the LOX-1 receptor by incubating with anti-LOX-1 antibody followed by goat anti-mouse IgG coupled to Texas Red and Chlamydia with FITC conjugated monoclonal antibody (green fluorescence). Co-localization was determined by confocal fluorescence microscopy using a LSM5 PASCAL Zeiss confocal microscope. Panel A - Staining of C. pneumoniae with the genus specific FITC conjugated CF2 antibody. Panel B - Staining of endothelial cells with anti-LOX-1 receptor monoclonal antibody. Panel C - Panels A and B are superimposed demonstrating extensive co-localization of C. pneumoniae and the LOX-1 receptor. Arrows highlight stained organism/cells.