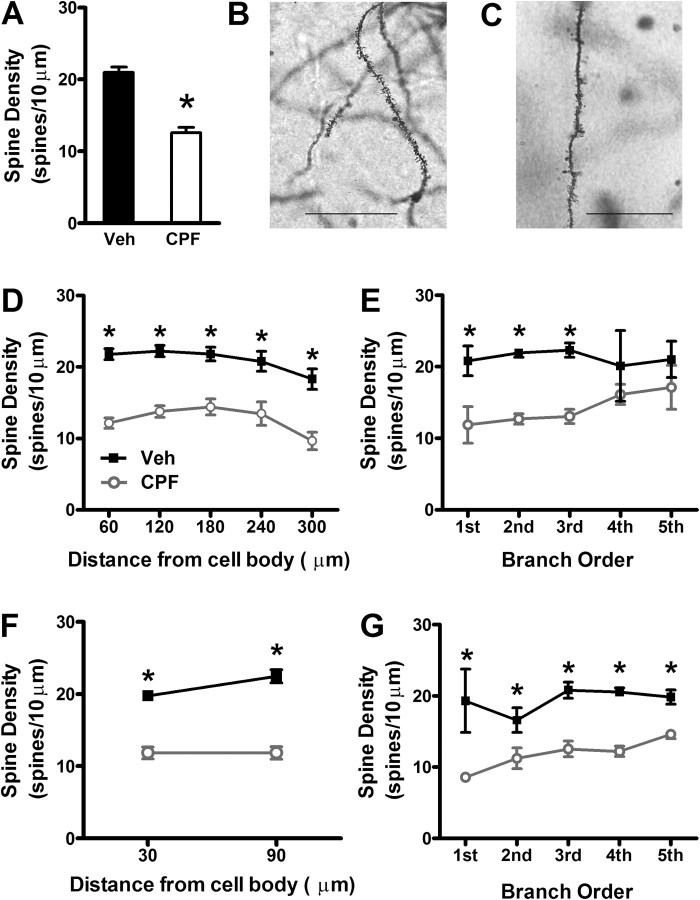
FIG. 7.
Spine density is dramatically decreased in CPF-treated mice compared with controls at 3 months following treatment. (A) Total spine density is decreased in CPF-treated mice compared with vehicle controls (*p < 0.001 compared with vehicle). Magnification of dendritic spines (×100) in Golgi-stained CA1 pyramidal neurons from vehicle-treated (B) and CPF-treated mice (C). Scale bars: 10 μm. The decrease in spine density of (D) apical dendrites (*p < 0.01 compared with vehicle) and (F) basilar dendrites in CPF-treated mice is not dependent on distance from soma (*p < 0.001 compared with vehicle). (E) The decrease in spine density of apical dendrites is significantly different from controls up to the third branch point (*p < 0.05 compared with vehicle). (G) The decrease in spine density of basilar dendrites in CPF-treated mice is not dependent on number branch points. For panels (D–G), data represent means ± SEM.