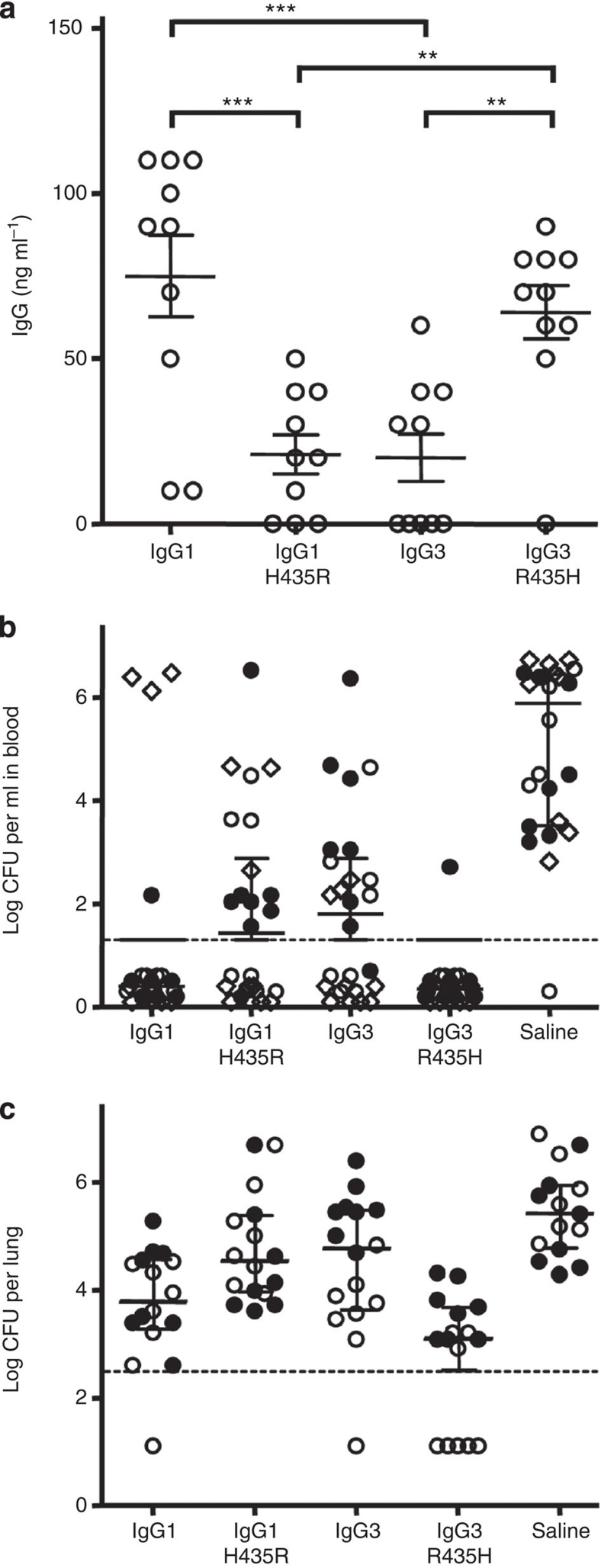
Figure 7. H435-containing IgG3 has increased serum persistence in mice and protects against pneumococcal pneumonia.
(a) Serum IgG levels 48 h after injecting 1 μg the IgG variants into outbred NMRI mice. IgG1–H435R and IgG3 show lower serum levels than IgG1 and IgG3–R453H. **P≤0.01; ***P≤0.001. (b) Three and (c) two experiments, showing outbred NMRI mice (8–10 per group per experiment) that were passively immunized intraperitoneally with 3 μg (circles symbols) or 1 μg (diamond) recombinant IgG anti-Streptococcus pneumoniae 6 or placebo 48 h before challenge with pneumococci of serotype 6A. Results from individual experiments are shown using the same symbol throughout (open or closed circles and diamonds). The number of bacteria found in (b) blood and (c) lungs 24 h after challenge are shown. (b) All but one mouse in the control group developed bacteremia, while all but four mice receiving WT IgG1 and all but one mouse receiving IgG3–R435H were completely protected. Approximately half of the mice receiving either IgG1–H435R or WT IgG3 developed bacteremia. (c) High numbers of bacteria were found in the lungs of control mice. All IgG-treated mice were significantly protected from lung infection, with lowered level of bacterial burden, with few mice in each group completely protected with no detectable bacteria. IgG3–R435H protected the mice significantly better than all other IgG variants, with five mice without detectable lung or blood infection. The dotted lines indicate the level of detection. Data in (a) represent the IgG levels in individual mice together with means and standard errors of means; data in (b,c) represent the bacterial load of individual mice together with medians (assuming the level of detection for individuals without detectable bacteria) and interquartile ranges, statistical comparison is tabulated in Table 1.