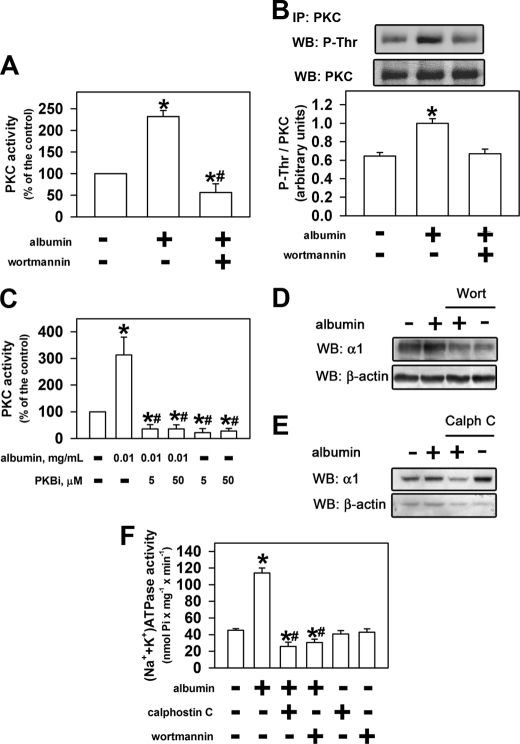
FIGURE 4.
PKC and PKB mediated the effect of albumin on the sodium pump. LLC-PK1 cells were kept overnight (D–F) or for 30 min (A–C) in medium depleted of serum in the absence or in the presence of 0.01 mg/ml albumin. After treatment, the cells were washed with PBS2+. A, effect of albumin on PKC activity in the presence or in the absence of 0.1 μm wortmannin (n = 5). B, effect of albumin on PKC phosphorylation in the presence or in the absence of 0.1 μm wortmannin. When indicated, PKC was immunoprecipitated (IP) followed by immunoblotting (WB) for phosphothreonine residue (P-Thr) or PKC (n = 3). C, modulation of the effect of albumin on PKC activity by PKB inhibitor (PKBi; n = 6). D and E, effect of albumin on the α1 subunit of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase expression in the presence or in the absence of 0.1 μm wortmannin or 0.1 μm calphostin C. The α1 subunit bands were quantified and normalized by β-actin expression (n = 4). F, modulation of the effect of albumin on (Na+ + K+)-ATPase activity by 0.1 μm wortmannin or 0.1 μm calphostin C. *, statistically significant in relation to the control (in the absence of albumin) or #, to 0.01 mg/ml albumin (p < 0.05).