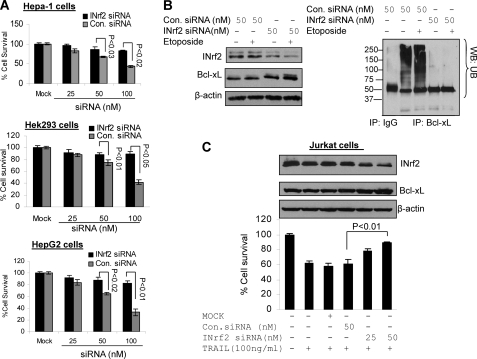
FIGURE 10.
siRNA-mediated knockdown of INrf2 stabilized Bcl-xL and promoted etoposide- or TRAIL-mediated cell survival. A, cell survival assay. Hepa-1, Hek-293, and HepG2 cells were plated at a density of 5000 cells/well in 24-well plates and transfected with control or INrf2 siRNA. The cells were then treated with etoposide (Hepa-1 cells (20 μm), Hek-293 cells (1 μm), and HepG2 cells (30 μm)) for 36 h. Cells were incubated with fresh MTT solution for 2 h at 37 °C, and absorbance at 570 nm was measured. B, Hepa-1 cells were transfected with control or INrf2 siRNA (50 μm) for 24 h and then treated with DMSO or etoposide (20 μm) for 36 h and harvested. Sixty μg of the lysates were immunoblotted (left). One mg of the same cell lysates was immunoprecipitated with anti-Bcl-xL antibody, and immune complexes were Western blotted for anti-ubiquitin (UB) antibodies (right). C, cell survival assay. Jurkat cells were plated at a density of 5000 cells/well in 24-well plates and transfected with control siRNA or INrf2 siRNA as indicated for 24 h. The cells were then treated with human recombinant TRAIL protein (100 ng/ml) for 30 h. Cells were incubated with fresh MTT solution for 2 h at 37 °C, and absorbance at 570 nm was measured (bottom). From the same experiments, 8 μg of Jurkat cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-INrf2, anti-Bcl-xL, and anti-β-actin antibodies (top). Each data point represents a mean ± S.D. and is normalized to the value of the corresponding control cells. Error bars, S.E.