FIGURE 2.
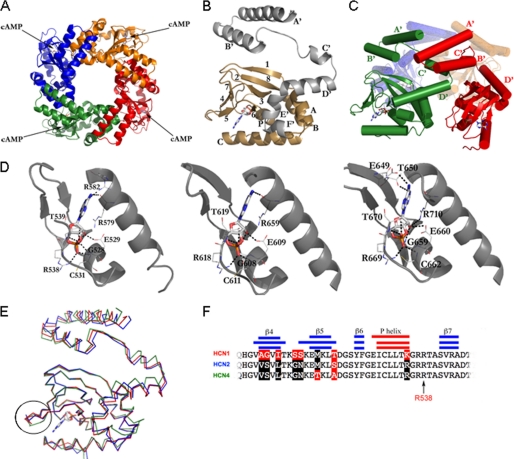
Crystal structure of the soluble portion CB (C-linker plus CNBD) of HCN1 bound to cAMP. A, HCN1CB tetramer viewed parallel to the 4-fold axis. Each subunit is shown in a different color. B, the protomer of HCN1CB with cAMP. The C-linker, helices A′–F′, is in gray; the CNBD, β-sheets 1–8 and helices A, B, P, and C, is in gold. C, subunit-subunit interactions mediated in the tetramer by the C-linker; helices A′ and B′ form a helix-turn-helix motif that interacts with the helix-turn-helix motif formed by the C′ and D′ helices of the neighboring subunit. The C-linker of one monomer (red) contacts two other subunits in the tetramer (green and orange). Cylinders and arrows represent helices and strands, respectively. D, from left to right, cAMP binding site of HCN1CB, HCN2CB, and HCN4CB, showing hydrogen bonds and salt bridges that stabilize the cAMP molecule. The binding amino acids are conserved among the three HCN isoforms. In particular, six polar contacts are strictly preserved between the same atoms (see supplemental Table II for the list of interactions). In addition, the residue Cys-531 (HCN1) makes a salt bridge (not present in the other two isoforms) between its nitrogen and the O1P of the cAMP, stabilizing the cyclic nucleotide inside the binding pocket. Another stabilizing element is the polar contact between residue Arg-582 (Arg-659 in HCN2 and Arg-632 in HCN4) and the atom N1 of the cAMP. The same atom contacts residue Arg-579, fundamental for the affinity for the cNMP (27). Also visible in our HCN2 structure are two more polar contacts (not reported in Ref. 11) between the atoms O2* and O2P (cAMP) and the nitrogen atoms of the residues Cys-611 and Gly-608, completing the range of strictly preserved amino acids mentioned above. E, differences in the structures highlighted by the superimposition of HCN1CB (red), HCN2CB (blue), and HCN4CB (green). The β4-β5 loop at the entrance of the cAMP binding site in the CNBD is circled. F, alignment of the amino acid sequences of the three proteins in the circled region. Secondary structures are indicated by the blue/red bars. Residues identical in HCN1 and HCN2 (black) but different in HCN1 (red) are highlighted. The conserved arginine, Arg-538 in HCN1, important for cAMP binding, is indicated by an arrow.