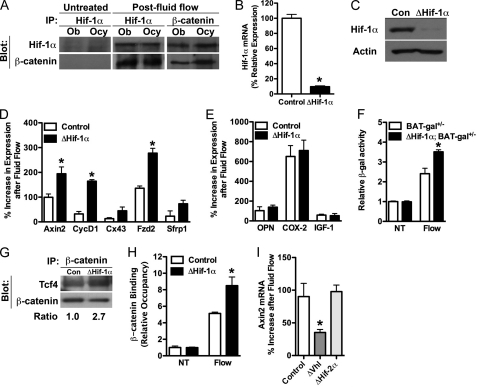
FIGURE 5.
Hif-1α antagonizes load-induced β-catenin signaling. A, co-immunoprecipitation (IP) revealed that Hif-1α and β-catenin interact in both primary osteoblasts (Ob) and MLO-Y4 (Ocy) cells after exposure to fluid flow. B and C, primary osteoblasts isolated from Hif-1α floxed mice were infected with adenovirus expressing Cre recombinase to abolish Hif-1α expression (B) and prevent its induction after fluid flow exposure (C). Con, control. D and E, osteoblasts deficient for Hif-1α (ΔHif-1α) exhibited increased expression levels of β-catenin target genes (D), but not osteopontin (OPN), Cox-2, or IGF-1 (E), after exposure to fluid flow. F, BAT-gal reporter activity was increased in osteoblasts rendered deficient for Hif-1α and exposed to fluid flow. NT, untreated. G and H, an increased association of β-catenin with Tcf4 (G) and increased binding to the Axin2 promoter (H) were evident in ΔHif-1α osteoblasts after exposure to fluid flow in co-immunoprecipitation and ChIP assays, respectively. I, overexpressing Hif-1α by disrupting the expression of Vhl inhibited Axin2 expression after fluid flow exposure, whereas disrupting Hif-2α expression was without effect. Data are plotted mean ± S.E. *, p < 0.05