Fig. 2.
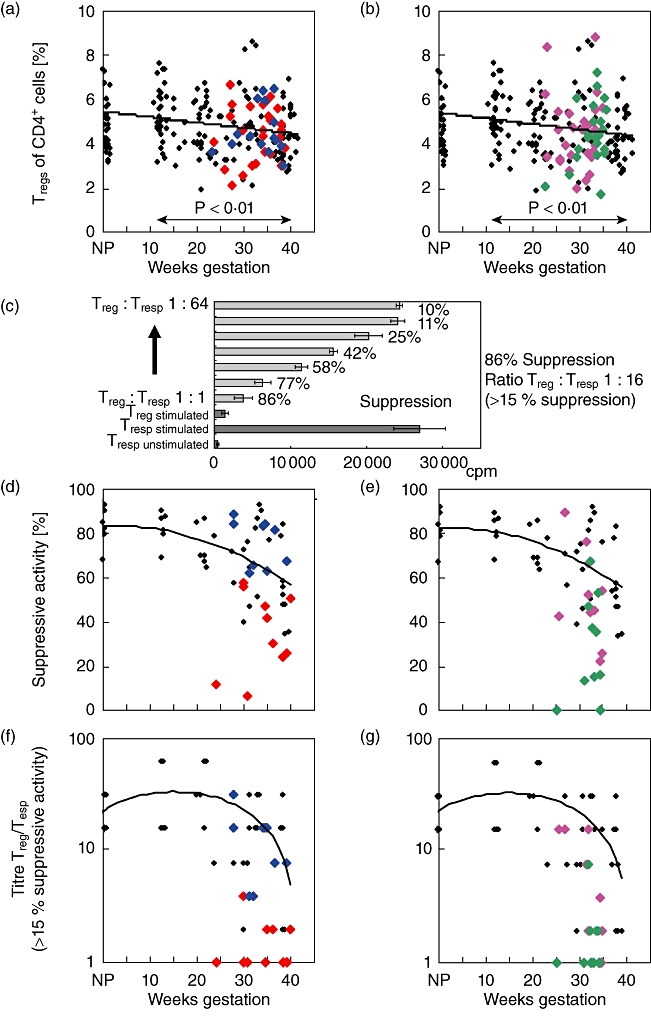
Detection of CD4+CD127low+/−CD25+forkhead box protein 3 (FoxP3+) Treg cells and their suppressive activity in healthy and complicated pregnancies. The percentage of CD4+CD127low+/−CD25+FoxP3+ Tregs of total CD4+ T cells was estimated in pregnancies affected by pre-eclampsia ( ) or HELLP syndrome (
) or HELLP syndrome ( ) (a), and in pregnancies affected by CI (
) (a), and in pregnancies affected by CI ( ) or PL (
) or PL ( ) (b), in comparison to healthy pregnancies (♦). CD4+CD127low+/−CD25+ Treg cells were isolated by the magnetic affinity cell sorting (MACS) technique and their suppressive activity was examined using suppression assays (c) (see Methods). The figure shows the maximum suppressive activity (Treg/Tresp = 1/1) (d,e) and the ratio of Treg/Tresp (titre) up to which the purified Treg cells could be diluted to achieve a minimum suppressive activity of at least 15% (f,g). The diagrams represent the individual data and the regression line obtained for healthy non-pregnant volunteers (group a; n = 6), healthy pregnancies during the normal course of pregnancy (groups 1–4; n = 36), pregnancies affected by pre-eclampsia (group 5, n = 10) or HELLP syndrome (group 6; n = 9) (d,f) and pregnancies affected by CI (group 7, n = 10) or PL (group 8; n = 10) (e,g). Compared to healthy third-trimester women (groups 3 and 4), the suppressive activity of the isolated CD4+CD127low+/−CD25+ Tregs from women with pre-eclampsia (group 5) and from women with PL (group 8) was reduced significantly, concerning both the maximum suppressive activity (P < 0·01) and the ratio of Treg/Tresp up to which a minimum suppressive activity of 15% could be achieved (P < 0·001). CI: cervical insufficiency; PL: preterm labour necessitating preterm delivery; HELLP syndrome: haemolysis-elevated liver enzyme level-low platelet count syndrome.
) (b), in comparison to healthy pregnancies (♦). CD4+CD127low+/−CD25+ Treg cells were isolated by the magnetic affinity cell sorting (MACS) technique and their suppressive activity was examined using suppression assays (c) (see Methods). The figure shows the maximum suppressive activity (Treg/Tresp = 1/1) (d,e) and the ratio of Treg/Tresp (titre) up to which the purified Treg cells could be diluted to achieve a minimum suppressive activity of at least 15% (f,g). The diagrams represent the individual data and the regression line obtained for healthy non-pregnant volunteers (group a; n = 6), healthy pregnancies during the normal course of pregnancy (groups 1–4; n = 36), pregnancies affected by pre-eclampsia (group 5, n = 10) or HELLP syndrome (group 6; n = 9) (d,f) and pregnancies affected by CI (group 7, n = 10) or PL (group 8; n = 10) (e,g). Compared to healthy third-trimester women (groups 3 and 4), the suppressive activity of the isolated CD4+CD127low+/−CD25+ Tregs from women with pre-eclampsia (group 5) and from women with PL (group 8) was reduced significantly, concerning both the maximum suppressive activity (P < 0·01) and the ratio of Treg/Tresp up to which a minimum suppressive activity of 15% could be achieved (P < 0·001). CI: cervical insufficiency; PL: preterm labour necessitating preterm delivery; HELLP syndrome: haemolysis-elevated liver enzyme level-low platelet count syndrome.
