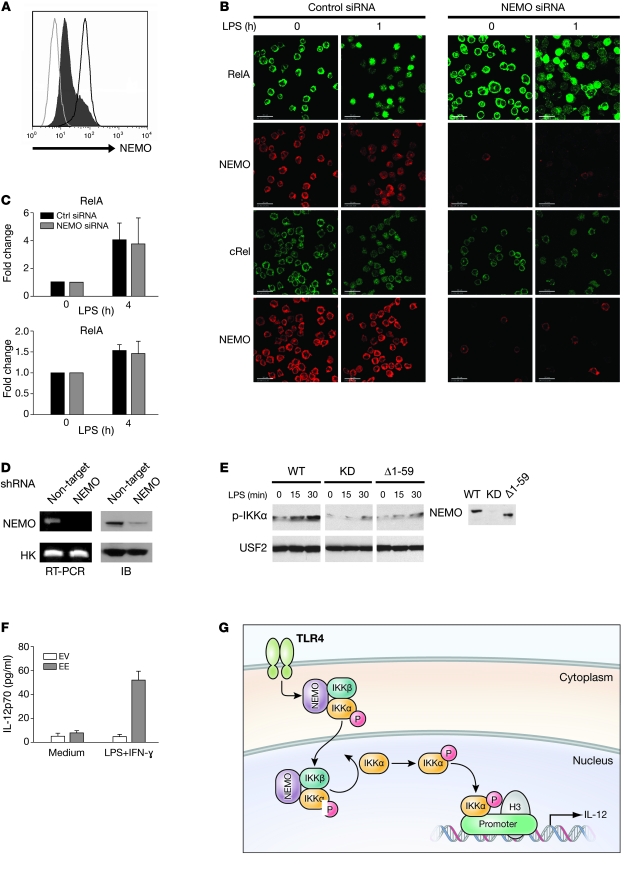
Figure 7. Complementation experiments in THP1 cells.
(A) THP1 cells were transfected with either control siRNA (dark gray line) or NEMO siRNA (black histogram), and residual NEMO expression was determined by flow cytometry. Isotype-matched control antibody staining is represented by the light gray line. (B) Nuclear translocation of NF-κB in siRNA-transfected THP1 was assayed by confocal microscopy. THP1 cells transfected either with control siRNA (left panels) or NEMO siRNA (right panels) were stimulated with LPS (2.5 μg/ml) for 60 minutes and then stained with either anti-RelA (green) or anti-cRel (green) antibody. Anti-NEMO antibody (red) was also used to assess NEMO expression in visualized cells. Scale bars: 30 μm. (C) RelA and cRel DNA–binding activity was measured in cellular extracts prepared from LPS-stimulated NEMO knockdown THP1 cells by ELISA. Mean and SD of 3 independent experiments are displayed. Ctrl, control. (D) NEMO expression determined by either immunoblot and semiquantitative PCR in THP1 cells transduced with either nontargeting or NEMO-targeting shRNA-expressing lentivirus. (E) A direct interaction between NEMO and IKKα is necessary for nuclear IKKα phosphorylation. THP1 NEMO knockdown (KD) cells were reconstituted with WT, empty vector, or a truncated form of NEMO that lacks IKKα binding. Following LPS stimulation for the indicated time, nuclear extracts were prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis with phospho-IKKα/β or USF2 antibodies. A Western blot of cellular NEMO levels is shown in the right panel. (F) IL-12p70 measurements in supernatants from THP1 NEMO knockdown cells transfected with either IKKα (EE) or empty vector (EV) following stimulation with LPS (2.5 μg/ml) plus IFN-γ (2,000 U/ml). (G) Proposed model for the dual function of NEMO in the NF-κB signaling pathway. Upon LPS stimulation, the pool of phosphorylated IKK complexes constitutively enter the nucleus, where they can phosphorylate IKKα. Activated nuclear IKKα phosphorylates histone H3 on the promoters of several NF-κB–responsive genes to mediate gene transcription.