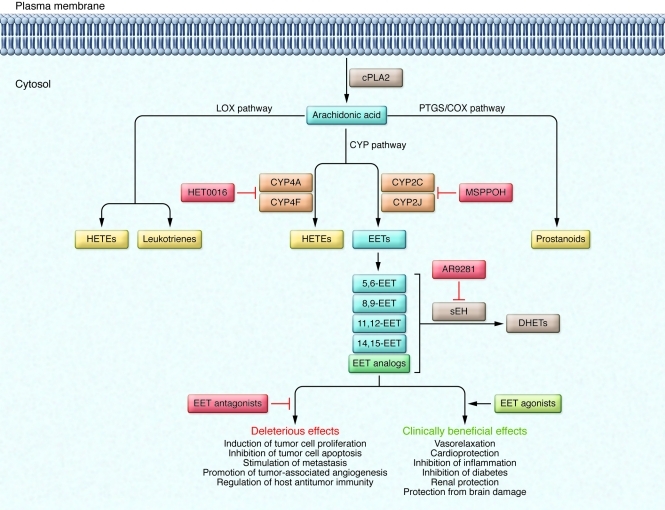
Figure 1. An overview of CYP epoxygenase pathways and how they can be modulated.
AA is a polyunsaturated fatty acid that constitutes the phospholipid domain of most cell membranes. It is liberated from cellular membranes by cPLA2. Free AA can be metabolized through three major pathways: the PTGS/COX pathway, the LOX pathway, and the CYP pathway. In the CYP pathway, AA is converted to EETs and HETEs by CYP epoxygenases and CYP ω-hydroxylases, respectively. The EETs are then further metabolized to less active DHETs by sEH. MSPPOH is a selective inhibitor of CYP epoxygenases, and HET0016 is a selective inhibitor of CYP ω-hydroxylases. AR9281 is a selective inhibitor of sEH and is currently under evaluation in phase II clinical trials as a treatment for patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes.