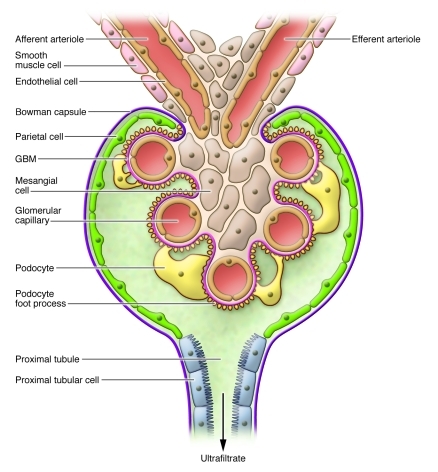
Figure 1. Major structural components of the glomerulus, the filtering unit of the kidney.
A key function of the kidneys is to filter the blood, removing waste products and regulating electrolyte concentrations and acid-base balance. The blood is filtered by individual nephrons, composed of the glomerulus (the filtering unit) and the tubules, which reabsorb most of the ultrafiltrate. The glomerulus consists of a capillary bed composed of specialized endothelial cells, mesangial cells, podocytes, and the GBM. The fenestrated endothelial cells, the podocytes, and the GBM form the glomerular filtration barrier.