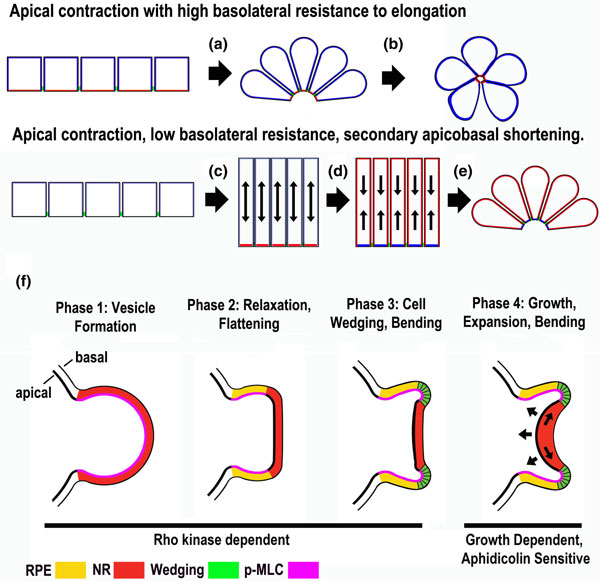
Figure 1.
Sectional diagrams showing modes of epithelial bending. During monophasic epitheilial bending apical contraction occurs with relatively high basolateral resistance to cell elongation (a,b). In the biphasic mode, apical contraction occurs in the presence of relatively low resistance to elongation (c); this is followed by a second phase of apical-basal shortening in the presence of contracted apices, which results in bending (d,e) [2,3,5]. (f) Sectional diagrams illustrating bending of the neural retina epithelium in a stem cell-derived mammalian optic vesicle in culture [6]. RPE = retinal pigment epithelium; NR = neural retina; p-MLC = phosphorylated myosin light chain.