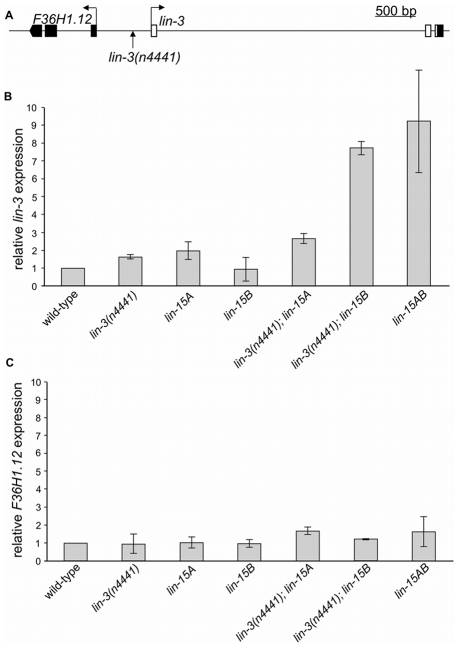
Figure 2. The lin-3(n4441) mutation specifically prevents repression of lin-3.
(A) The lin-3(n4441) mutation is located 211 bp upstream of the lin-3 transcript. The gene F36H1.12 is upstream of lin-3 in the opposite orientation, and lin-3(n4441) is located 465 bp from the predicted F36H1.12 transcript. Solid boxes, exons; open boxes, UTRs. (B) lin-3 mRNA levels in lin-3(n4441) single and double mutants. As reported previously [27], lin-3 mRNA levels are substantially increased in lin-15AB double mutants but not in lin-15A or lin-15B single mutants. Like other class A synMuv mutations, lin-3(n4441) caused a substantial increase in lin-3 mRNA levels only in a class B synMuv mutant background. Realtime RT-PCR experiments were performed using RNA harvested at the late L2 or early L3 stage from each strain shown. Relative lin-3 mRNA levels were normalized to the levels of mRNA encoding the ribosomal protein subunit rpl-26 using the ΔΔCt method [52]. The means and standard deviations of relative lin-3 mRNA levels from two independent trials are shown. The lin-15A(n767), lin-15B(n744) and lin-15AB(e1763) alleles were used in this experiment. (C) F36H1.12 mRNA levels in synMuv single and double mutants. No combination of lin-3(n4441), lin-15A, and lin-15B mutations affected F36H1.12 mRNA levels. Realtime RT-PCR experiments were performed using RNA harvested at the late L2 or early L3 stage from each strain shown. Relative F36H1.12 mRNA levels were normalized to the levels of mRNA encoding the ribosomal protein subunit rpl-26 using the ΔΔCt method. The means and standard deviations of relative F36H1.12 mRNA levels from two independent trials are shown.