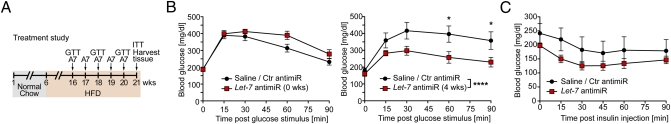
Fig. 5.
AntimiR-induced repression of Let-7 expression improves impaired glucose tolerance. (A) Design of the diabetes treatment study. Six-wk-old C57BL/6 mice were fed for 10 wk with HFD. Subsequently, the mice were maintained on an HFD for 5 more wk, but half of the mice (n = 5) were treated with Let-7 antimiR (once weekly 20 mg/kg body weight) whereas control animals (Ctr) received either saline (n = 3) or control antimiR (n = 2). (B) GTTs (1.5 mg glucose/g body weight) were performed before initiation of antimiR treatment (Left) and at 4 wk after the first antimiR injection (Right). *P < 0.05; ****P < 0.0001 for Ctr (saline + control antimiR) vs. Let-7 antimiR– treated mice by ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest. (C) An ITT was performed at 1 wk after the last Let-7 antimiR injection. Blood glucose levels were measured at baseline and at 15, 30, 45, 60, and 90 min after i.p. insulin injection (1.0 U/kg body weight).