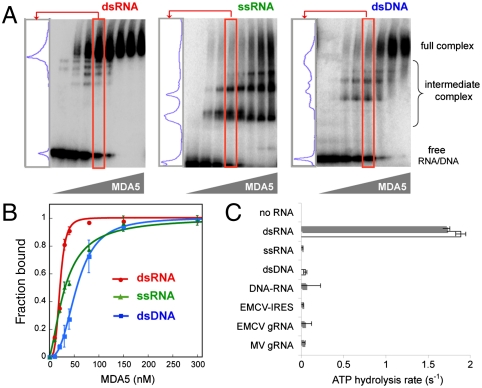
Fig. 1.
Only binding of MDA5 to dsRNA is cooperative and stimulates ATP hydrolysis. (A) EMSA with 112 bp/nt dsRNA, ssRNA, and dsDNA. A lane in which approximately 50% of MDA5 is bound to the respective nucleic acid (red box) was chosen for each sample, and the distribution of the complexes is displayed in the left-hand panel. (B) The EMSA results in A were fit to the Hill equation to obtain dissociation constant (Kd) and Hill coefficient (Nh). Estimated Kd and Nh are 22 nM and 4.0 for dsRNA, 33 nM and 1.5 for ssRNA, and 57 nM and 2.7 for dsDNA, respectively. Plotted values are mean ± SD (n = 2). (C) ATP hydrolysis rates (mean ± SD, n = 4) of MDA5 (0.3 μM) free of nucleic acids, MDA5 bound to 112 bp/nt dsRNA, ssRNA, dsDNA, DNA–RNA hybrid (▪ sequence 1, □ sequence 2, see Table S1), IRES (1 kb), and genomic RNA (gRNA) (∼7 kb) of EMCV and MV. Equivalent mass concentration (4.8 μg/mL) was used for all nucleic acids.