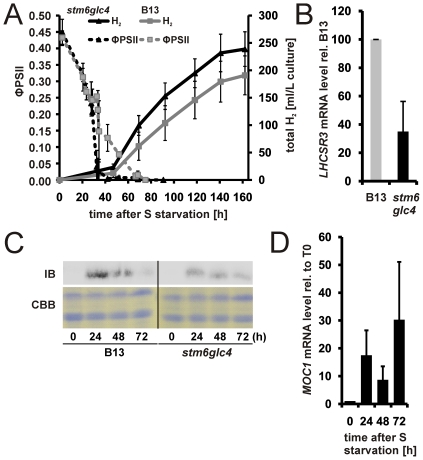
Figure 8. Complementation of stm6glc4 with a functional MOC1 gene reduces hydrogen production and restores LHCSR3 accumulation.
A: Representative H2 measurement with B13 and stm6glc4. The change in the photosynthetic quantum yield (ΦPSII; left y-axis; dotted lines) was recorded along with the total amount of H2 produced by both cultures (total H2; right y-axis; continuous lines). On the x-axis the time after sulfur depletion is indicated. B13 (squares) is shown in grey and stm6glc4 (triangles) in black. B: Abundance of LHCSR3 mRNA after 40 hours of sulphur starvation in B13 (grey bar) and stm6glc4 (black bar) determined by RT-Q-PCR. The mRNA level of B13 was set to 100% and standard deviations indicated by error bars represent three different experiments. C: Immunodetection of LHCSR3 in samples of B13 and stm6glc4 after sulphur depletion with indicated duration times. The upper panel shows an anti-LHCSR3 immunoblot (IB) and the lower one a Coomassie-stained gel serving as a loading control (CBB). D: RT-Q-PCR analysis of the MOC1 mRNA expression in WT samples taken at different time points after (24, 48 72 h) and before (0 h) sulphur depletion. Expression is given relative to T0, which was set to 1.