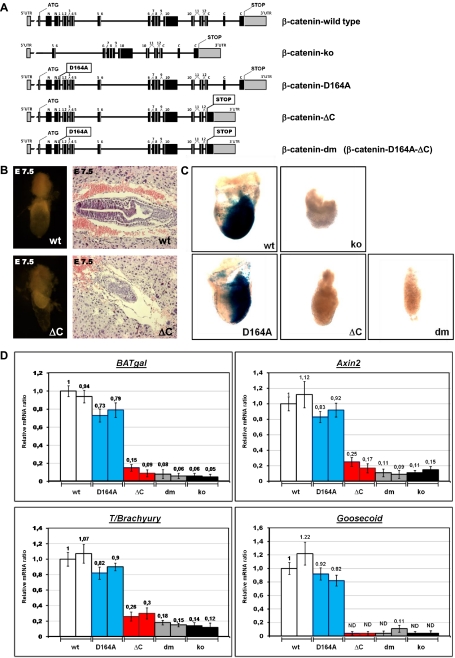
Figure 3.
Contribution of the C-terminal β-catenin coactivators is essential for gastrulation. (A) Schematic representation of the β-catenin loci of the mutant strains generated. β-Cateninko was generated by crossing a CMV-Cre line with a conditional β-catenin strain (β-cateninflox/flox; i.e., B6.129-Catnbtm2Kem/J); the resulting allele does not contain an in-frame ATG, and exons 2–6, which encode domains essential for binding to E-cadherin and/or TCF/LEF, are eliminated. β-Catenin-D164A harbors a single-amino-acid exchange (D164A) in exon 4, preventing the interaction between the resulting β-catenin and BCL9/BCL9L. In the β-catenin-ΔC locus, a preliminary stop codon is followed by a frameshift introduced into exon 13; moreover, exon 15 was directly fused to exon 13, thus eliminating exon 14. The β-Catenin-dm strain carries both individual mutations. Boxes represent exons, with black indicating coding and gray indicating noncoding; numbers denominate the Arm repeats. (B) Morphology of wild-type (wt) and β-cateninΔC/ΔC (ΔC) embryos at E7.5, including extraembryonic tissues. (Right panels) Embryos dissected from decidual tissues. (Left panels) Sagittal sections of E7.5 embryos within the decidua stained by H&E. (C) Developmental failure during gastrulation caused by C-terminal truncation of β-catenin is associated with absence of TCF/β-catenin-mediated transcription, as monitored by the Wnt-specific reporter BAT-gal. Dissected embryos at E7.5; each individual embryo inherited one allele of the BAT-gal transcriptional reporter and is homozygous for the indicated mutant allele of β-catenin. (ko) Total loss of β-catenin. LacZ expression from the BAT-gal reporter was determined using enzymatic staining based on X-gal (blue). (D) Transcription of Wnt/β-catenin target genes (transgenic reporter BAT-gal and endogenous genes Axin2 and T/Brachyury) is strongly reduced in E6.5 embryos homozygous for the β-catenin allele that prevents the binding of β-catenin to C-terminal transcription coactivators (ΔC). Expression of factors regulating mesoderm formation (T/Brachyury and Goosecoid) is also strongly affected in β-cateninΔC/ΔC embryos. Levels of mRNA were determined by quantitative real-time PCR and normalized to the housekeeping genes SDHA and GAPDH. The levels of a β-cateninwt/wt (wild-type) embryo are set as 1. Embryos from two independent litters were tested for each homozygous β-catenin mutant as indicated. (dm) Double-mutant form; (ko) β-catenin-null embryos. Each embryo carries one allele of the BAT-gal reporter. Error bars show standard deviation. (ND) Nondetectable levels.