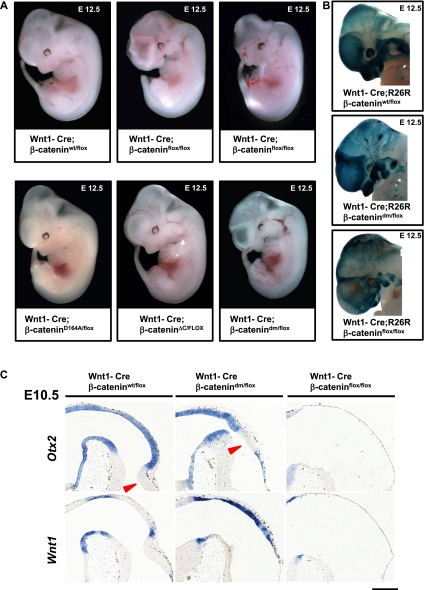
Figure 5.
Total loss of β-catenin in Wnt1-Cre-expressing tissues leads to more severe phenotypes than blocking the Wnt signaling output of β-catenin. (A) E12.5 embryos expressing Wnt1-Cre, one conditional allele of β-catenin (β-cateninflox), and a second allele of β-catenin as indicated. In Wnt1-Cre; β-cateninflox/flox embryos, Cre activity results in the absence of β-catenin in Wnt1-expressing tissues. Such embryos show strong defects in craniofacial development, midbrain, and hindbrain. The phenotype of Wnt1-Cre; β-catenindm/flox embryos is milder compared with that of Wnt1-Cre; β-cateninflox/flox, especially in the case of telencephalic lobes and midbrain and hindbrain areas. Representative embryos are shown. (B) X-gal staining visualizing Wnt1-Cre-mediated recombination using R26R in the heads of embryos at E12.5. The strong dark-blue signal in forming craniofacial structures (jaw/maxilla and meninges) and pharyngeal arches in wild type represents neural crest derivatives. Similarly strong signals could be partially observed in Wnt1-Cre/R26R; β-catenindm/flox, while in Wnt1-Cre/R26R; β-cateninflox/flox, there are fewer, irregularly scattered X-gal-positive cells. (C) In situ hybridization with early midbrain–hindbrain junction markers on sagittal sections of embryonic heads at E10.5. (Top left panel) In wild-type embryos, the transcription factor Otx2 is expressed in the midbrain with a sharp boundary at the midbrain–hindbrain junction. (Top middle panel) In Wnt1-Cre; β-catenindm/flox, the midbrain–hindbrain junction marked by Otx2 expression is shifted, and the prospective cerebellum is not developed. (Bottom left panel) Wnt1 is expressed in wild type in the posterior midbrain and along the dorsal midline. (Bottom middle panel) Wnt1-Cre; β-catenindm/flox animals show increased expression of Wnt1 along the dorsal midline. (Right panels) In contrast, Wnt1-Cre; β-cateninflox/flox (ko) brains lack expression of both Otx2 (top) and Wnt1 (bottom), indicating absence of any midbrain and cerebellar structures. The arrowheads point to hindbrain structures (cerebellum). Bar, 200 μm.