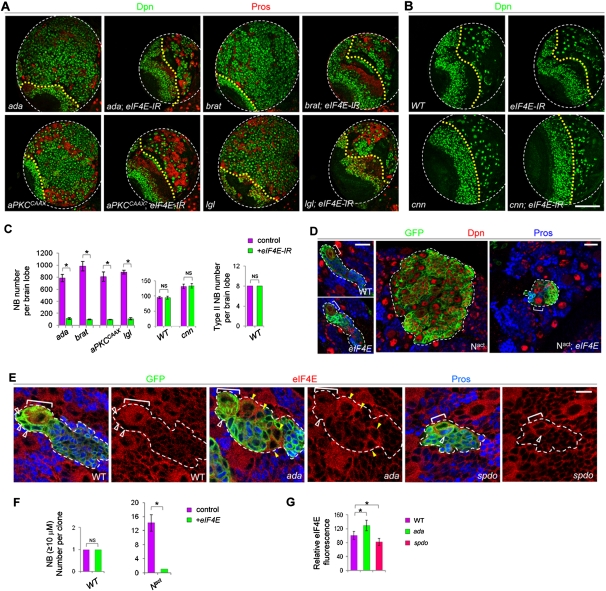
Figure 3.
eIF4E knockdown efficiently and specifically inhibits brain tumor formation. (A) Effects of NB-specific knockdown of eIF4E (driven by 1407-GAL4) on ectopic NB formation in ada, brat, or lgl mutants or aPKCCAAX overexpression backgrounds. (Green) NBs marked by Dpn; (red) neurons marked by Pros. Posterior views of a single brain lobe are shown. (B) eIF4E knockdown has no discernable effects on normal NB development or on ectopic NB formation resulting from symmetric division of type I NBs in cnn mutants. From this panel on, the yellow dotted line marks the boundary between the optic lobe (left) and the central brain (right) areas. Central brain NBs can be distinguished from optic lobe NBs based on their medial/superficial location in the brain and larger size. (C) Quantification of data from A and B. (*) P < 0.0001; n = 15–20. (D) Clonal analysis of type II NBs in wild-type, eIF4E mutant, Nact, or Nact; eIF4E backgrounds. (E) eIF4E expression (red) in wild-type, ada, or spdo mutant type II NBs. (F,G) Quantification of data from D and E. Bars: A,B, 100 μm; D, 20 μm; E, 10 μm.