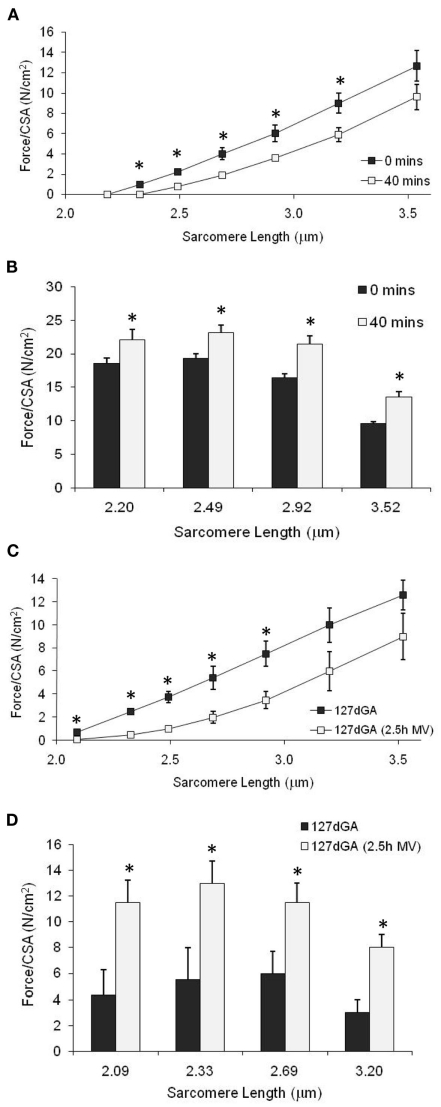
Figure 5.
Effect of spontaneous air breathing or mechanical ventilation on passive tension and maximum Ca2+-activated tension in diaphragm fibers from 127-day gestation and term fetuses. (A,B) Passive tension and maximum force at increasing sarcomere length for fibers from term diaphragm where fetuses either did not breathe (0 min) or had been spontaneously breathing for 40 min; n = 4 fetuses, 12 fibers, each treatment group. (C,D) Passive tension and maximum force at increasing sarcomere length for fibers from 127 day gestation diaphragm where the fetuses had been subjected to either no, or 2.5 h mechanical ventilation; n = 3 fetuses, 12 fibers, each treatment group. *P < 0.05, between treatment group comparison.