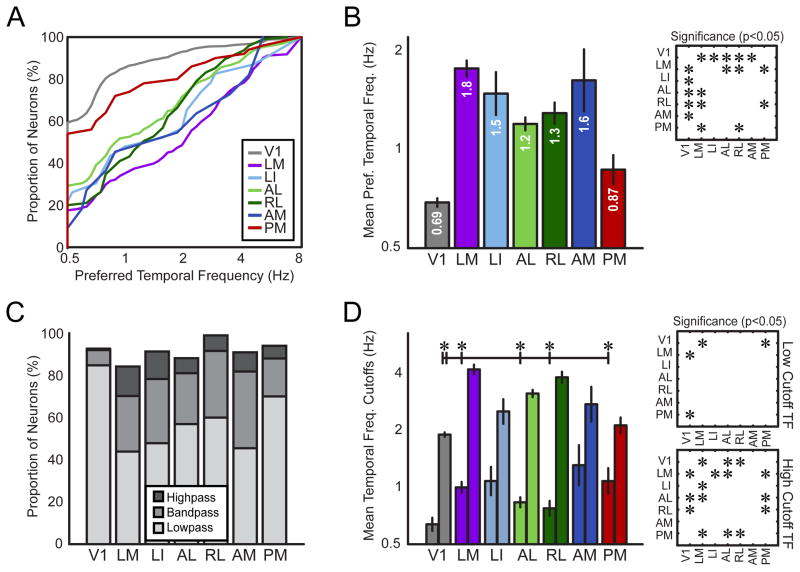
Figure 4. Encoding for temporal frequency information differs across visual areas.
(A) Cumulative distributions of preferred temporal frequency (TF) for each visual area (inset color-coding for each area corresponds to all panels). (B) Geometric mean preferred TF for each visual area. (C) Proportions of highpass, bandpass and lowpass neurons for each area. (D) Geometric mean TF cutoffs show the range of TFs encoded by each population on average. For each area, the left bar indicates the low cutoff TF and the right bar indicates the high cutoff frequency. Asterisks and lines above plot indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between V1’s high cutoff frequency and the low cutoff frequency of extrastriate areas. Insets in (B) and (D) show statistical significance (p < 0.05) of pair-wise comparisons between areas, corrected for multiple comparisons using the Tukey-Kramer method. Error bars are standard error of the mean (S.E.M.) in (B, D). TF bandwidth comparisons are in Figure S4.