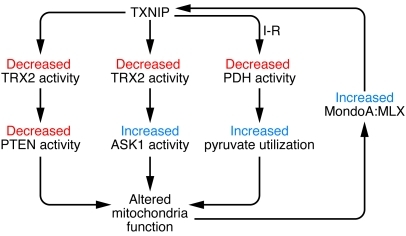
Figure 1. TXNIP regulates mitochondrial function via several pathways.
First, TXNIP regulates fuel use in the mitochondria via inhibition of TRX2 and alteration of PTEN-Akt signaling. Second, TXNIP translocates to the mitochondria in response to changes in cellular redox state, resulting in inhibition of TRX2 and subsequent activation of ASK1 that leads to opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Third, as shown by Yoshioka et al., TXNIP interacts with PDH and acts as a metabolic switch between aerobic and anaerobic metabolism (4). Last, TXNIP expression is closely regulated by the MondoA:MLX transcription factor, which is activated by glucose uptake, glycolytic intermediates generated by the mitochondria, and lactate.