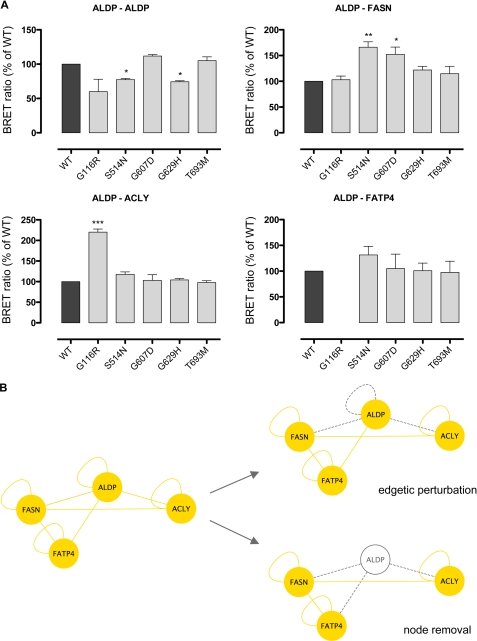
FIGURE 5.
Disease-causing mutations in the ABCD1 gene lead to edgetic perturbations and are prone to node removal. A, BRET experiments analyzing the impact of ABCD1 gene mutations on binary interactions of ALDP. WT ALDP was compared with ALDP constructs representing disease-causing missense mutations (G116R, S514N, G607D, G629H, and T693M); homomeric interactions as well as interactions with FASN, ACLY, and FATP4 were determined. BRET ratios are given as percent WT of n = 4 independent experiments. No BRET ratio is given in cases of luciferase signals below a method-specific cutoff of 13,000. B, schematic illustration of the consequences of disease-causing mutations in ABCD1 on the PPI network established by wild-type ALDP (yellow lines). Missense mutations can induce distinct molecular phenotypes affecting individual PPI (edgetic perturbations, gray dashed line) or the availability of the ALDP protein (node removal, gray node).