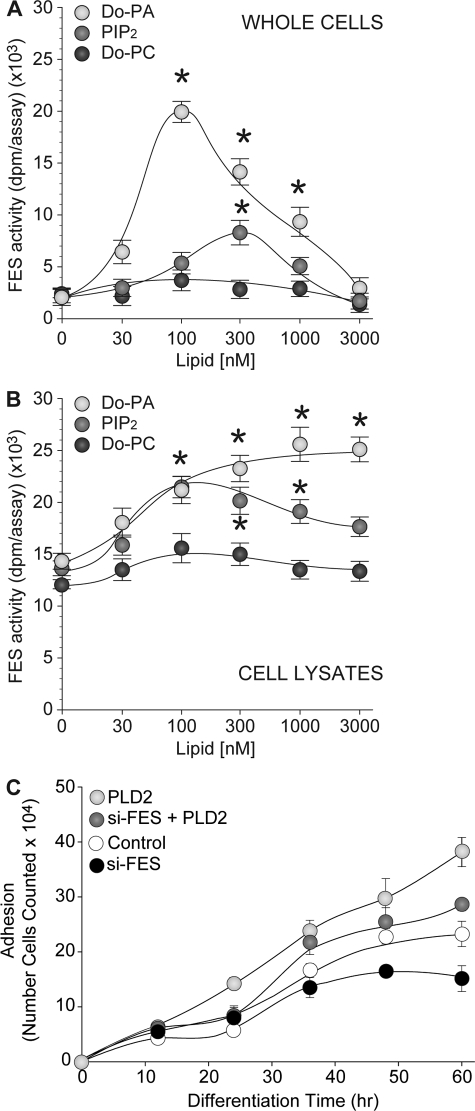
FIGURE 8.
PA and PIP2 but not PC activate Fes kinase activity. A, HL-60 cells growing in suspension were incubated with the indicated concentration of dioleoylphosphatidic acid (Do-PA), phosphatidylinositol 4–5-bisphosphate (PIP2), or dioleoylphosphatidylcholine (Do-PC) for 20 min. After incubation, cell lysates were obtained and 20 μg were analyzed for kinase activity associated with Fes. B, in vitro activation of Fes kinase activity. Protein extracts of untreated HL-60 cells were obtained and 20 μg were assayed for the ability of dioleoylphosphatidic acid, PIP2, or dioleoylphosphatidylcholine to activate Fes-associated tyrosine kinase activity directly added to the kinase reaction media at the indicated concentrations. C, effect of PLD2 overexpression in differentiating THP-1 cells associated with Fes. THP-1 cells in suspension were mock-transfected or transfected with 2 μg of PLD2-WT plasmid DNA, 300 nm si-Fes, or both and were then induced to differentiate in fresh media containing 50 ng/ml PMA. Differentiated (adhered) cells were immediately fixed in 24-well plates after PMA treatment (time 0) and at varying times post-induction of differentiation (12–72 h). Adhesion assay results are the means ± S.E. from three independent experiments conducted in duplicate. The symbols * and # denote statistically significant (p < 0.05) differences between PLD2 overexpression or silenced samples and controls, respectively.