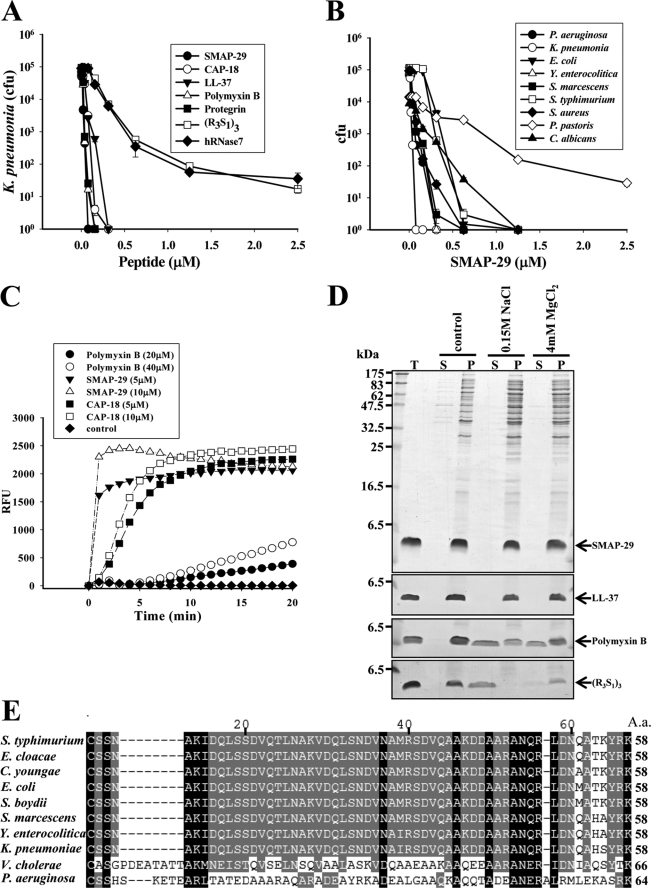
FIGURE 1.
Antimicrobial spectra of cationic AMPs and their target protein on Gram-negative bacteria. A, bactericidal activities of AMPs on K. pneumoniae are shown. B, antimicrobial activity of SMAP-29 on various microbes is shown. Microbes (5–10 × 104 cfu) were treated with AMPs at 37 °C in 10 mm sodium phosphate, pH 7.5, for 3 h and then plated on agar plates for the determination of remaining cfu. C, increase of membrane permeability of K. pneumoniae after AMP treatment is shown. Bacteria (107 cfu) were incubated with 1 μm SYTOX® Green in a dark 96-well plate for 15 min before the addition of AMP. The increase of fluorescence was measured using 485- and 520-nm filters for excitation and emission wavelengths, respectively. RFU, relative fluorescence units. D, binding of AMPs to K. pneumoniae is shown. Overnight cultures of bacteria (107 cfu) were incubated with SAMP-29, LL-37, Polymyxin B, or (R3S1)3 (3 μg each) in 50 μl at 37 °C for 30 min, then spun at 10,000 × g for 10 min followed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie Blue staining. NaCl or MgCl2 was added as indicated. T represents total AMPs employed, S is for supernatant, and P is for pellet. E, amino acid sequence alignment of Lpp-homologous proteins by the software ClustalX is shown. The Lpp sequences of S. typhimurium (NP_460342), Enterobacter cloacae (YP_003612855), Citrobacter youngae (ZP_06353081), E. coli (NP_416192), Shigella boydii (YP_001880438), S. marcescens (AAA26566), Y. enterocolitica (YP_001006405), K. pneumoniae (YP_001335792), V. cholerae (ZP_01972724), and OprI sequence of P. aeruginosa (NP_251543) were obtained from National Center for Biotechnology Information.