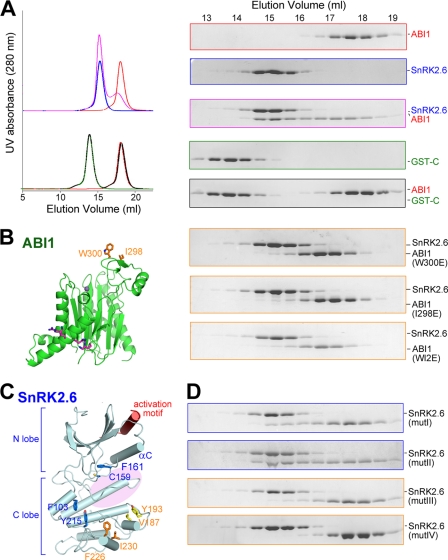
FIGURE 4.
Identification of the second interface between SnRK2.6 and ABI1. A, SEC analyses of the interactions between ABI1 and the FL or domain II of SnRK2.6. The same elution fractions of each SEC injection were applied to SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie Blue staining. FL SnRK2.6 is non-tagged, whereas domain II is GST-fused. B, SEC analyses showed that ABI1 variants containing point mutations of W300E, or I298E, or W300E/I298E (WI2E) were unable to form stable complex with SnRK2.6. C, selection of hydrophobic residue clusters on the surface of SnRK2.6 that may be involved in ABI1 interaction. Four clusters, whose residues are shown in sticks, were selected on the basis of the crystal structure of SnRK2.6. The likely position of the activation loop, which is invisible in the crystal structure, is indicated by the pink shadow. D, SEC analyses of the interactions between ABI1 and SnRK2.6 variants. Refer to the main text for the annotation of mutI–IV.