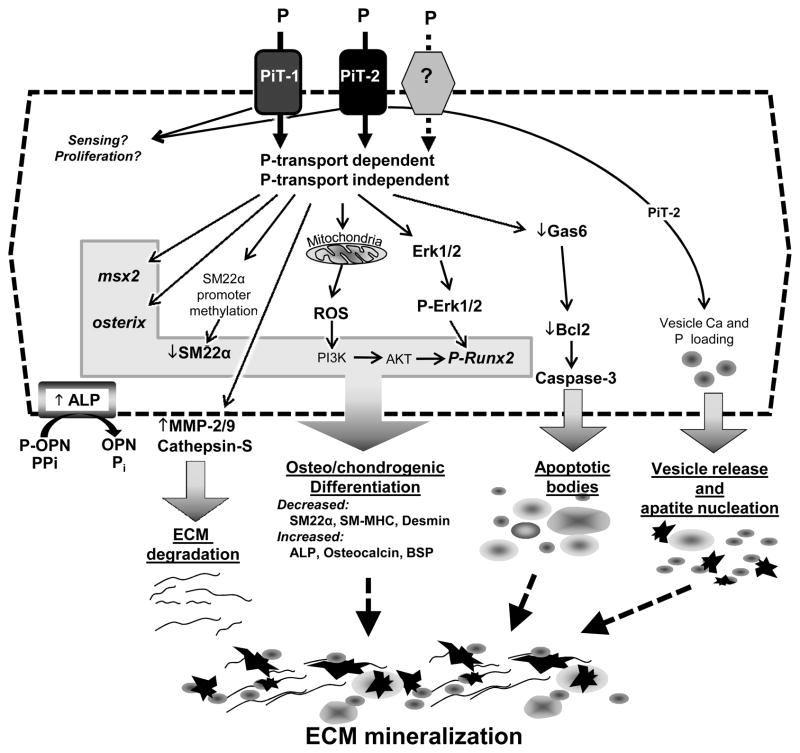
Figure 3. Role of P in VSMC Calcification.
Elevated extracellular P affects multiple signalling pathways that increase the susceptibility of VSMC to calcification including decreased calcification inhibitors, increased ECM degradation, osteo/chondrogenic differentiation, apoptosis and vesicle release. Some of the effects of P are mediated through sodium dependent phosphate co-transporters, Pit-1 and Pit-2, potentially via P transport-dependent and -independent activities. Whether other receptors exist that mediate specific downstream signalling pathways in response to P is not yet known, but cannot be excluded.