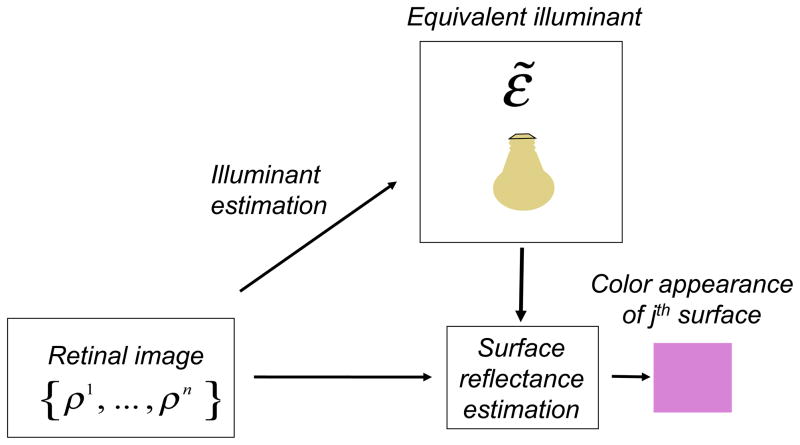
Figure 3. Equivalent illumination models.
The information available about the scene (the retinal image {ρ1,…, ρn}) is used to form an estimate ε̃ of the illuminant coordinates, the equivalent illuminant. This estimate in turn determines how the color signal reflected from each scene surface is transformed to the perceptual representation that is color appearance.