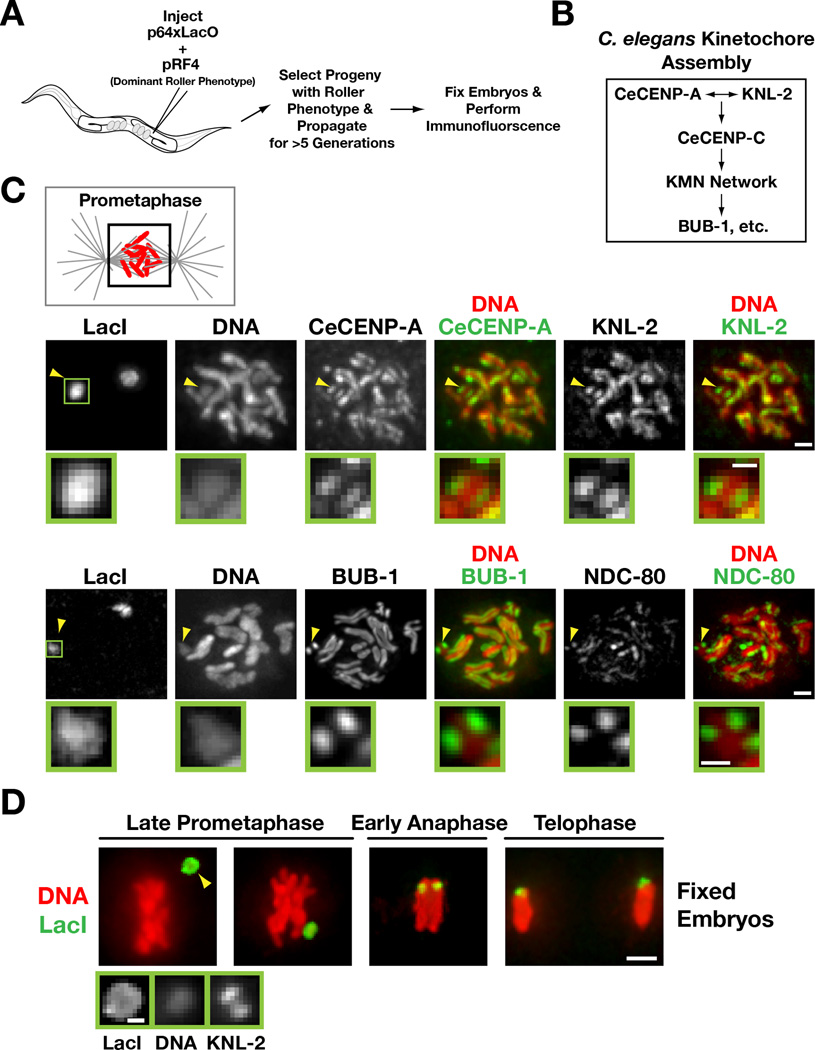
Figure 1. Kinetochores are present on extrachromosomal arrays that have been propagated for multiple generations.
A) Schematic of experimental strategy to analyze array structure by immunofluorescence.
B) Simplified hierarchy of C. elegans kinetochore assembly. The KMN network is comprised of KNL-1, the MIS-12 complex, and the NDC-80 complex.
C) Chromatin-associated inner kinetochore components CeCENP-A and KNL-2 (top row), the microtubule-binding outer kinetochore protein NDC-80 and the spindle checkpoint kinase BUB-1 (bottom row) localize to opposing faces of LacO-containing extra-chromosomal arrays during prometaphase. Arrowheads point to the array; the boxed region is magnified below. Scale bar 1 µm (0.5 µm for magnified regions).
D) Immunofluorescence of the LacO-containing extra-chromosomal array (LacI) and DAPI staining during late prometaphase, early anaphase and telophase in embryos. Higher magnification view of the array (arrowhead) with KNL-2 staining is shown on the bottom. Scale bar 2 µm (0.5 µm for magnified regions).