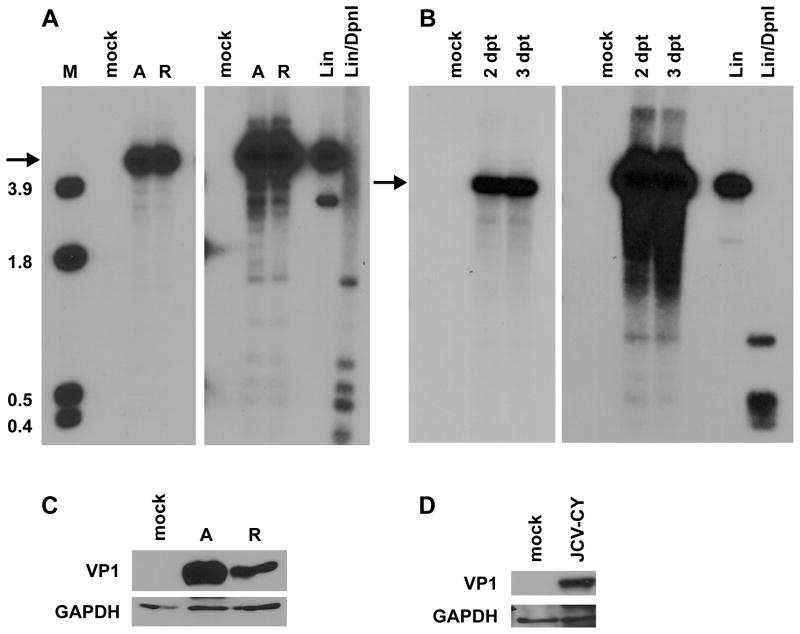
Fig 2.
Archetype BKPyV and JCPyV replicate efficiently in 293TT cells. A. 293TT cells were transfected with recircularized archetype (A) or rearranged (R) BKPyV genomes, and low molecular weight DNA was harvested at 4 dpt. Samples were linearized, digested with DpnI, and analyzed by Southern blotting. The right panel shows a darker exposure where the input DpnI digested bands and digested plasmid controls are visible. Arrow indicates the replicated viral genome. M, HindIII digest of pGEM-TU (size of bands in kb). Lin, linearized BKPyV plasmid control. Lin/DpnI, linearized and DpnI-digested BKPyV plasmid control. B. Low molecular weight DNA was harvested 2 and 3 dpt from archetype JCPyV transfection and analyzed by Southern blotting. Light and dark exposures are shown as in A. C, D. Analysis of VP1 expression. C. Total cell protein was harvested from 293TT cells 4 dpt and 90 μg of protein was analyzed by Western blotting for BKPyV VP1 and GAPDH expression. Mock, mock transfection. D. Total cell protein was harvested 4 dpt and 60 μg of protein was analyzed by Western blotting for JCPyV VP1 and GAPDH expression. The blots shown are representative of three independent experiments.