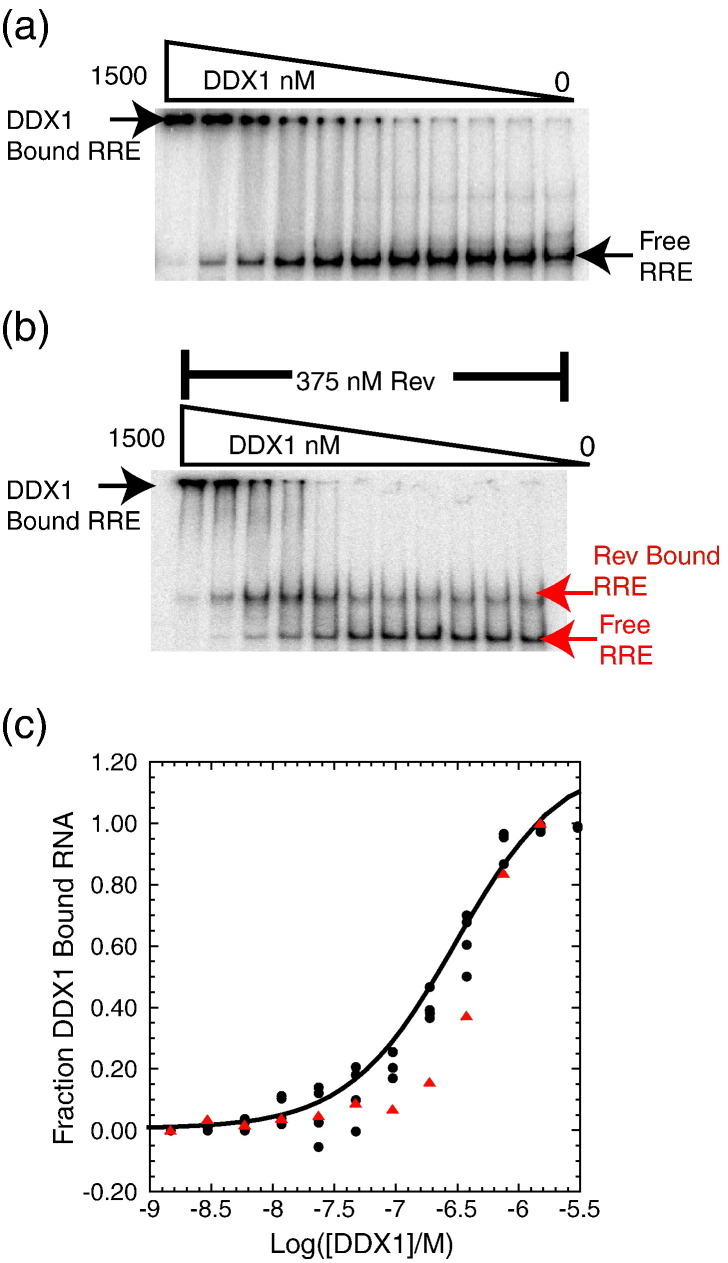
Fig. 6.
DDX1 and Rev bind independently to RRE RNA. (a) Electrophoretic gel mobility shift titration of DDX1 into radiolabeled RRE RNA, with the bands corresponding to free RRE, DDX1–RRE complex, and DDX1 concentration through the titration denoted. (b) DDX1 titration into radiolabeled RRE RNA in the presence of 375 nM Rev protein. Oligomeric Rev forms a tight complex with RRE RNA as indicated by the first shifted band. DDX1 binds independently to the Rev–RRE complex, seen as a supershifted band at increasing concentrations of DDX1. Bands corresponding to free RRE, Rev–RRE, and DDX1–Rev–RRE complexes are labeled. (c) Plot showing the fraction of DDX1 bound to labeled RRE RNA or Rev–RRE complex as a function of DDX1 concentration. The fraction of bound DDX1 was calculated as the disappearance of free RRE where black circles represent the direct titration of DDX1 in three independent trials described in (a) and red triangles denote the disappearance of free RRE and Rev–RRE bands described in (b).