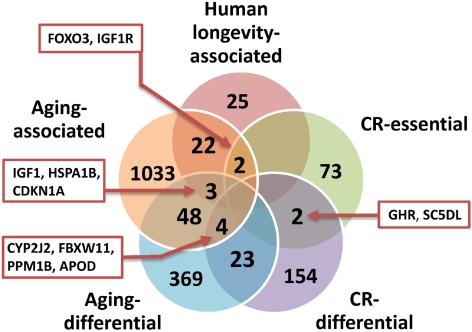
Fig. 2.
Overview and overlap of genes related to aging, human longevity, and CR. Shown are the intersections between human orthologs of genes identified via genetic manipulation experiments in model organisms (aging-associated), genes that disrupt or cancel life-extending effects of CR when mutated in model organisms (CR-essential), aging differentially expressed genes in mammals (aging-differential), CR-differentially expressed genes in mammals (CR-differential) and genes associated with human longevity in at least one epidemiological study (human longevity-associated). All data obtained from the GenAge database (http://genomics.senescence.info/genes/), except for the CR-associated genes, which come from data sets assembled by the authors from the literature, available on request.