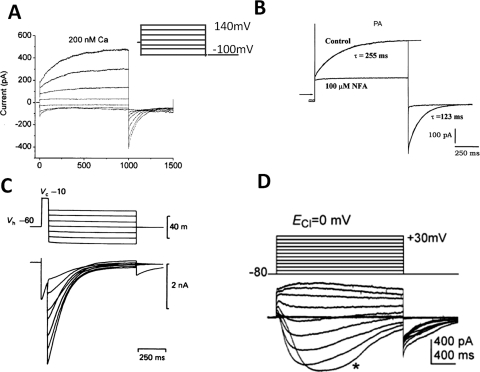
Fig. 1.
Examples of classic CaCCs recorded in X. laevis oocytes and mammalian cells. A, CaCC in X. laevis oocyte. The patches were clamped from a holding potential of 0 mV to potentials between 140 and −100 mV for 1 s, followed by a 500-ms pulse to −100 mV (Qu and Hartzell, 2000). B, CaCC recorded in rat pulmonary artery (PA) smooth muscle cells, representative current tracings recorded in the absence (Control) and presence of 100 μM NFA, voltage-dependent currents were evoked by 1-s step depolarization from a holding potential of −50 mV to +70 mV, followed by 1-s return steps to −80 mV (Greenwood et al., 2001). C, CaCC recorded in cultured rat dorsal root ganglia neurons activated by a depolarizing prepulse (Mayer, 1985). D, CaCC recorded in ICCs. ICCs were depolarized from −80 to +30 mV in 10-mV increments from a holding potential of −80 mV, and ECl− was adjusted to 0 mV (Zhu et al., 2009).