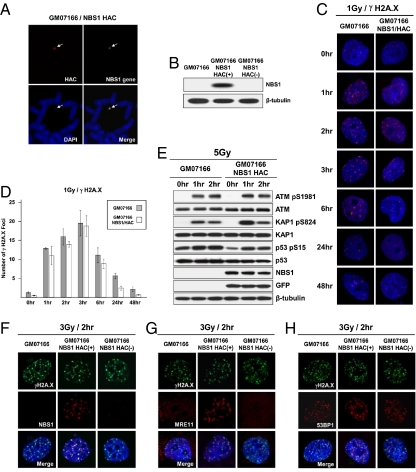
Fig. 3.
pNBS1 expression in NBS1-deficient cells. (A) FISH analysis of the alphoidtetO-HAC/NBS1 in GM07166 cells with specific probes for the BAC vector (red) and NBS1 gene sequences (green). (B) Western blot analysis of NBS1-deficient GM07166 cells, alphoidtetO-HAC/NBS1-containing GM07166 cells before and after HAC elimination from the cells by expression of the tTS fusion construct. (C and D) Kinetics of disassembly of γ-H2A.X foci in NBS1-deficient GM07166 cells and the same cells with alphoidtetO-HAC/NBS1. (C) Immunostaining of irradiated cells. Cells were stained with anti–γ-H2A.X antibodies (red) and with DAPI (blue) after exposition to 1 Gy IR and then collected after the times indicated. (D) Quantitative analysis of disassembly of γ-H2A.X foci. Cells were collected after the time indicated, and the average number of γ-H2A.X foci was quantified over time. (E) Western analysis of GM07166 cells and cells with alphoidtetO-HAC/NBS1. As predicted, p53, ATM, and KAP1 are phosphorylated in response to irradiation. (F–H) Analysis of colocalization of γ-H2A.X, MRE11, 53BP1, and NBS1 proteins after irradiation. NBS1-deficient cells (GM07166) and the same cells with alphoidtetO-HAC/NBS1 before and after HAC loss were fixed 2 h after irradiation with 3 Gy and were double-stained with anti–γ-H2A.X, anti-hMRE11, anti-53BP, and anti-hNBS1 antibodies. (F) NBS1 is colocalized with γ-H2A.X in cells carrying the alphoidtetO-HAC/NBS1. (G) γ-H2A.X and MRE11 are colocalized in foci in a pNBS1-dependent manner. (H) 53BP1 foci formation is not affected by absence of pNBS1.