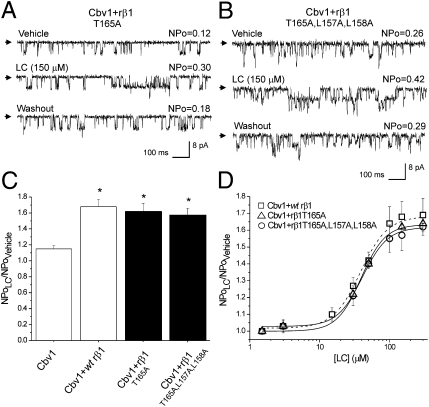
Fig. 3.
Ala substitutions in the proposed LC sensing site on the outer region of rβ1 TM2 domain do not ablate LC sensitivity of BK channels. Single-channel records from cbv1 + rβ1T165A (A) and cbv1 + rβ1T165A,L157A,L158A (B) channels show increases in BK NPo in response to LC. (C) Averaged responses to LC. *P < 0.05; significant from control (vehicle). (D) Concentration-response curves (CRCs) to LC on cbv1 coexpressed with WT rβ1, rβ1T165A, or rβ1T165A,L157A,L158A show similar characteristics: EC50 = 40.4, 39.3, and 40.8 μM, respectively, Emax ∼ 300 μM, and apparent Hill number (defined as the slope of the logit-log plot of LC action on channel steady-state activity) is ∼1.32 for each construct. Here and in all other figures, EC50 defines the LC required to obtain half-maximal increase in BK NPo by the steroid. Each point of CRC represents average from n ≥ 3.