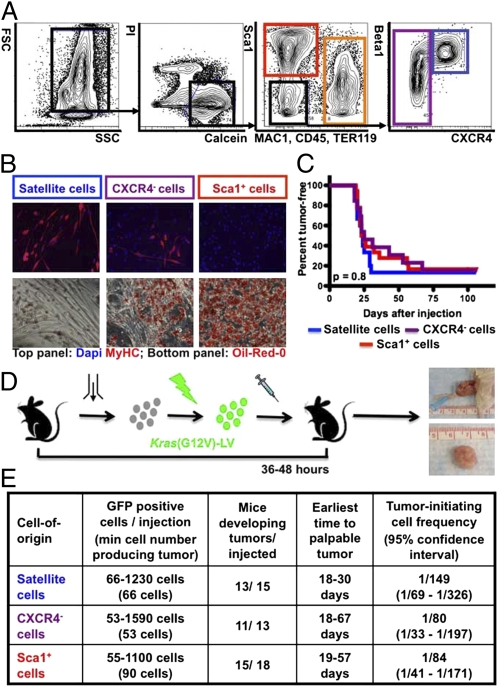
Fig. 1.
Tumor initiation by Kras(G12V)-expressing p16p19null MFA cells. (A) Mouse MFA cell subsets are discriminated by combinatorial staining for CD45, MAC1, Sca1, β1-integrin and CXCR4. (B) Differentiation of satellite cells (blue gate in A) and a subset of CXCR4− cells (purple gate in A) into myosin heavy chain-positive (MYHC+) myoblasts and myofibers (B, Upper). Differentiation of Sca1+ cells (red gate in A) and a subset of CXCR4− cells (purple gate in A) into Oil-Red-O+ adipocytes (B, Lower). (C and D) p16p19null MFA cells were infected with Kras(G12V) lentivirus and injected into the cardiotoxin-preinjured gastrocnemius muscles of NOD/SCID mice 36–48 h after cell isolation. Kaplan-Meier analysis (C) showed no differences in the percent of mice developing tumors (D) induced by individual cell types (P = 0.8). (E) Limiting dilution analysis showed equivalently high frequencies of tumor-initiating cells within each of the individual subsets of Kras(G12V)-transduced p16p19null MFA cells (P = 0.4). FSC, Forward Scatter; SSC, Side Scatter; Pi, Propidium Iodide; MAC1, Macrophage-1 antigen; TER119, antigen recognized by anti-Ly76 antibody; Sca1, stem cell antigen-1; CXCR4, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; Beta1, β1 integrin.