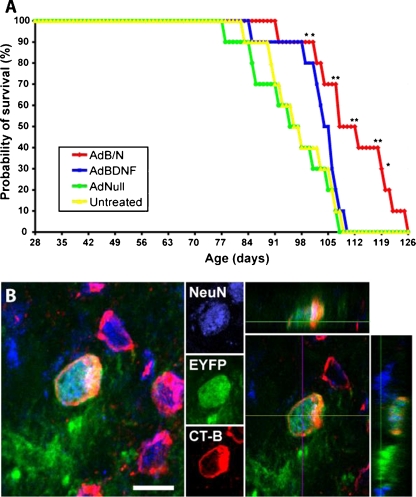
Fig. 3.
Induced striatal neurogenesis was associated with both anatomic integration and increased lifespan in R6/2 HD mice. (A) Adenoviral brain-derived neurotrophic factor (AdBDNF)/adenoviral Noggin (AdNoggin)-induced neurogenesis was associated with prolonged survival in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that the lifespan was significantly extended in R6/2 mice injected with AdBDNF/AdNoggin compared with R6/2 mice injected with AdBDNF only, or adenoviral Null (AdNull), or left untreated. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. (B) To trace the origins of the newly generated neurons, tamoxifen-treated Nestin-CreERT2/ROSA-EYFP bigenic mice (courtesy of Dr. Kageyama, [149]) received intraventricular infusion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and Noggin proteins followed by a resting period of 2 weeks to allow for differentiation and maturation. The mice also received intrapallidal injection of the retrograde tracer Alexa Fluor 555-conjugated Cholera Toxin subunit B (CT-B). Newly-generated neurons expressing the enhanced yellow fluorescent protein also expressed the mature neuronal marker, Neuronal Nuclei (NeuN), and integrated into the striato-pallidal circuitry as revealed by their incorporation of the fluorescent CT-B retrograde tracer. AdB/N = AdBDNF/AdNoggin. Scale bar = 10 μm